

By Qasim
Posted on May 15, 2025 | 11 min read
In today's fast-paced digital world, keeping websites secure and reliable is more important than ever for many website owners. Whether you're running a business or managing a personal site, understanding how a website is built can give you useful insights.
One of the best ways to dive deeper into a website's infrastructure is by using tools like WHOIS, query DNS, and SSL certificates. These tools help you monitor domain names, check ownership, ensure security, and spot potential threats before they grow.
This blog will show you how combining WHOIS data for a specific domain, DNS records, and SSL certificates can give you a full picture of a website's security, status, and ownership. We'll look at each tool separately and then explore how using them together can give you a more complete understanding of the websites you're examining.
Whether you're a cybersecurity expert aiming to reduce risks or a cybersecurity professional keeping an eye on domain data for security or competition, this guide will give you the knowledge you need to make smart decisions.
WHOIS data from the WHOIS database is a valuable tool for learning about a domain. It provides key details about a domain's name, registration, and owner, helping you understand its legitimacy, security, and ownership.
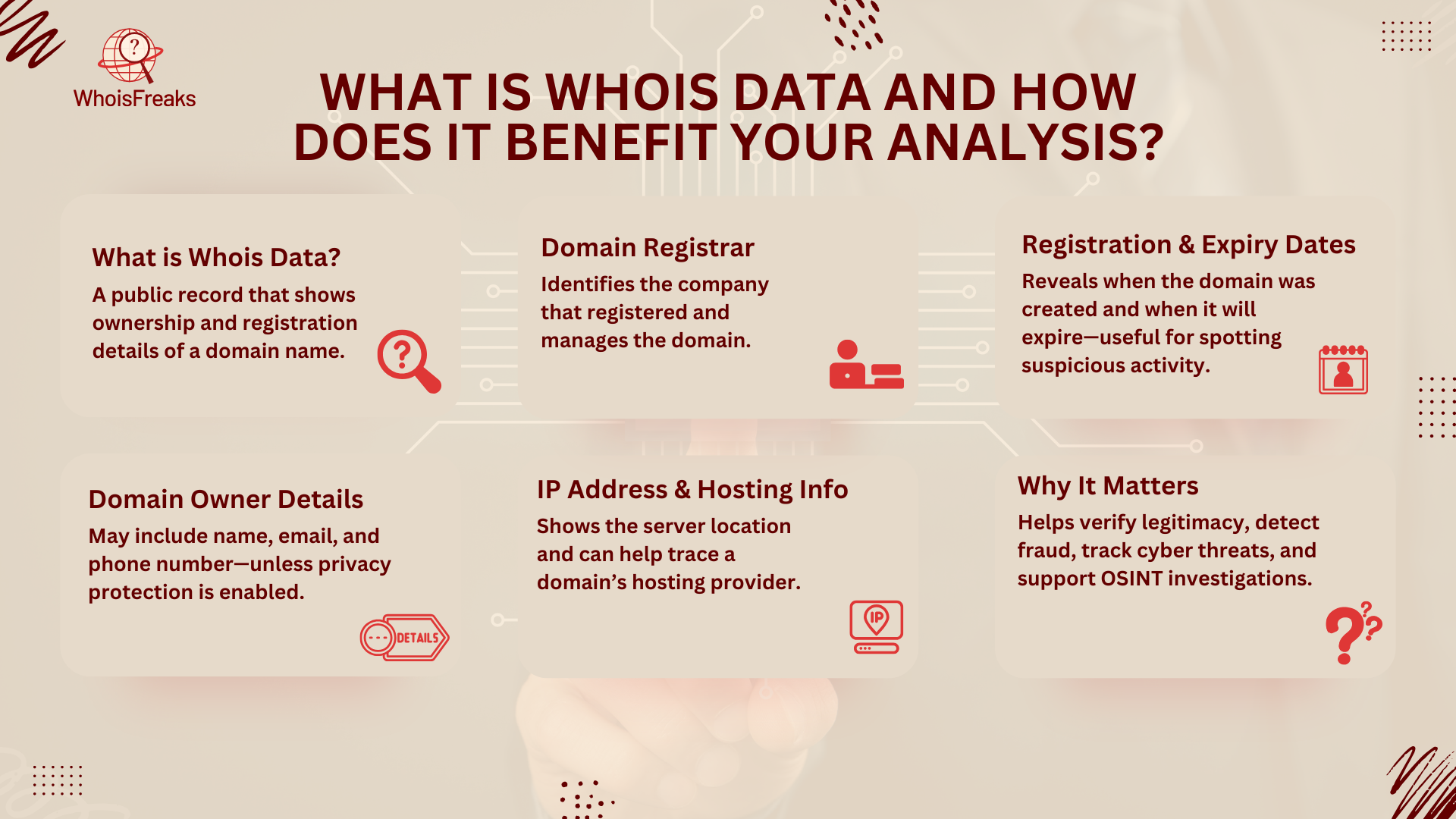
When you perform a WHOIS search, you get access to a record that contains important information, such as:
By reviewing WHOIS data, you can better understand a domain's ownership, uncover possible security issues, and spot expired domains that might be available for purchase. For instance, if a domain allows private registration, it might raise suspicions that the owner is hiding their identity for shady reasons.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the internet's address book. It helps turn domain names (like example.com) into IP addresses that computers use to connect with each other. Without DNS, we'd have to remember long and complicated IP addresses instead of easy-to-remember domain names.
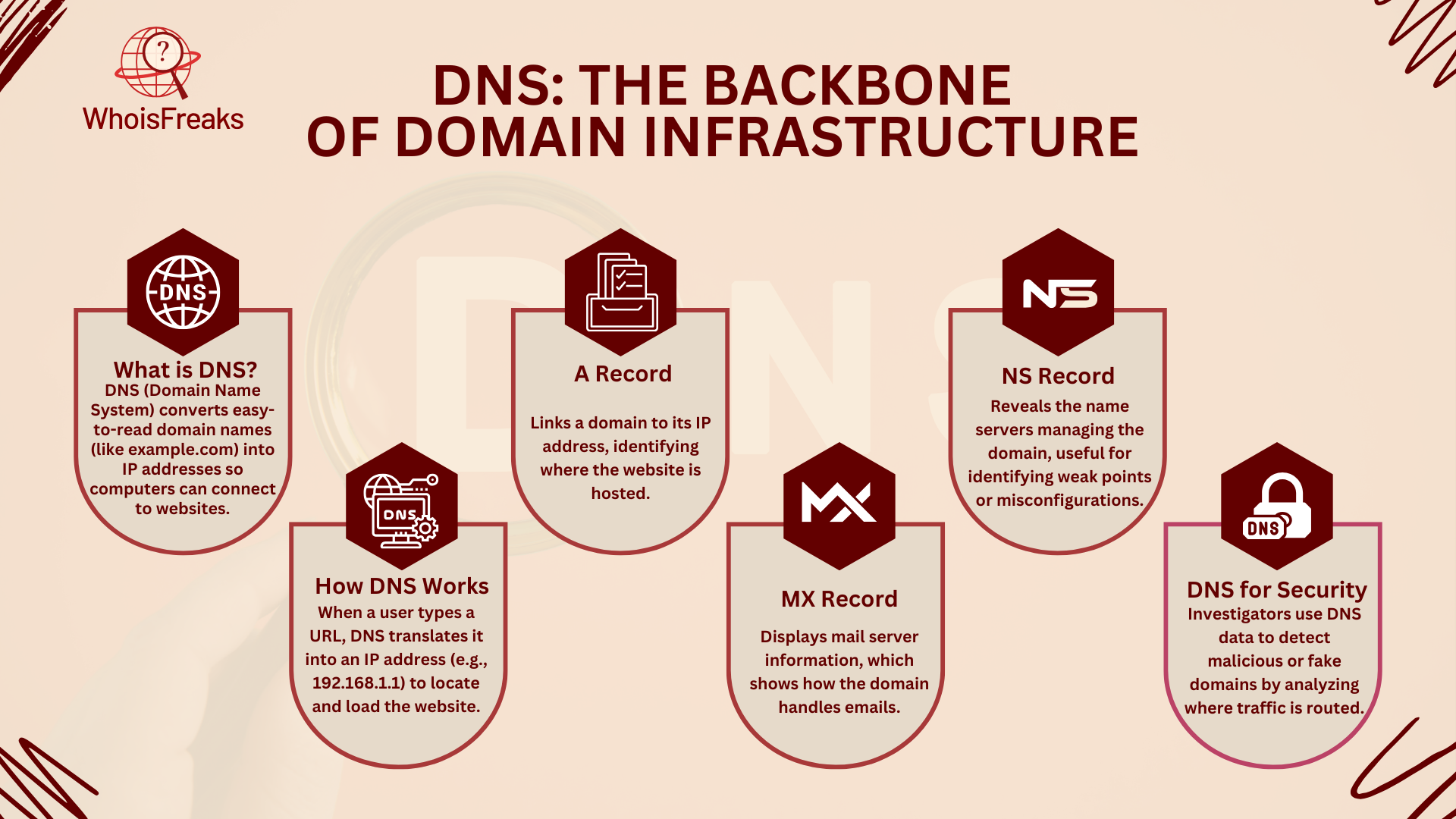
When you type a web address, like www.example.com, DNS quickly converts it into an IP address (like 192.168.1.1) that points to the website's server and sends packets of data. This process makes it easy for users to access websites without memorizing complex numbers.
Looking at DNS records can reveal details about how a website works and if it's secure. Some important DNS records include:
When paired with WHOIS data, DNS records give a fuller picture of a website's infrastructure, including essential services. While WHOIS reveals who owns the domain, DNS shows where it's hosted and how it interacts with other services like email.
Analyzing DNS data is also important for security. Cybersecurity experts use DNS records to spot fake domains or suspicious activities. For example, if a domain's DNS points to an unknown or risky server, it might indicate someone is trying to impersonate the site.
In today's digital world, SSL certificates (Secure Sockets Layer) have been crucial for protecting the data exchanged between your browser and a website for more than a decade. When you visit a site with HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), SSL certificates are what make the connection secure.
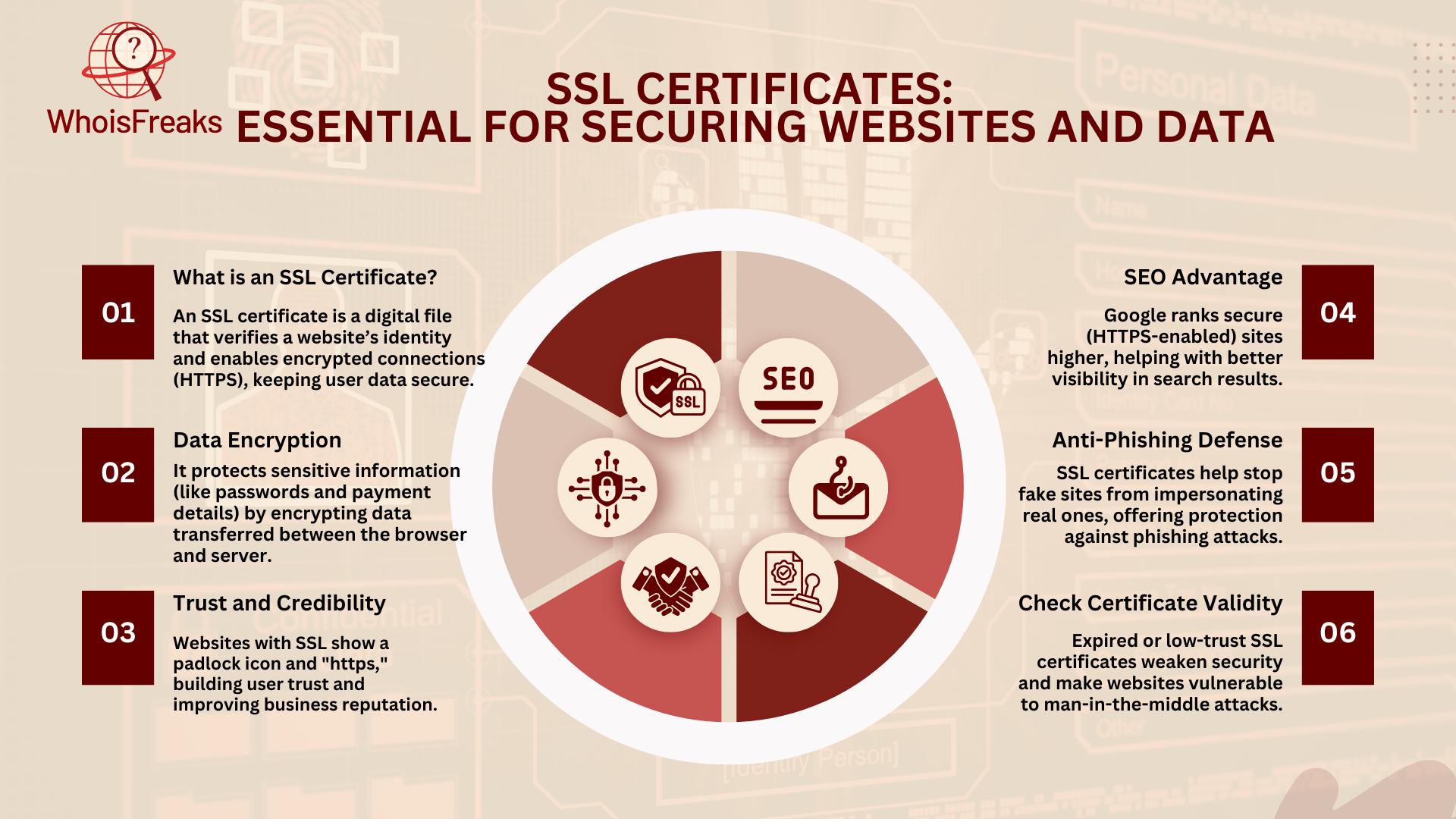
An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that verifies a website's identity and creates an encrypted connection with the client. This encryption keeps any data exchanged, like personal or payment information, safe from hackers.
SSL certificates are issued by an SSL provider and serve as a sign of trust. You can spot websites with SSL certificates by the padlock icon in the browser's address bar and the "HTTPS" in the URL, showing that the site is secure.
For cybersecurity experts or website owners, checking SSL certificate status is key. An expired certificate or one from a low-trust provider can leave a site open to man-in-the-middle attacks, where hackers intercept communications between the user and the site.
While WHOIS data, DNS records, and SSL certificates are useful on their own, combining all three gives you a much deeper understanding of a website's infrastructure, security, and potential risks.
Individually, each component reveals important details for different organizations, but when combined, they provide a more complete picture. Here's how each part contributes to the bigger picture:
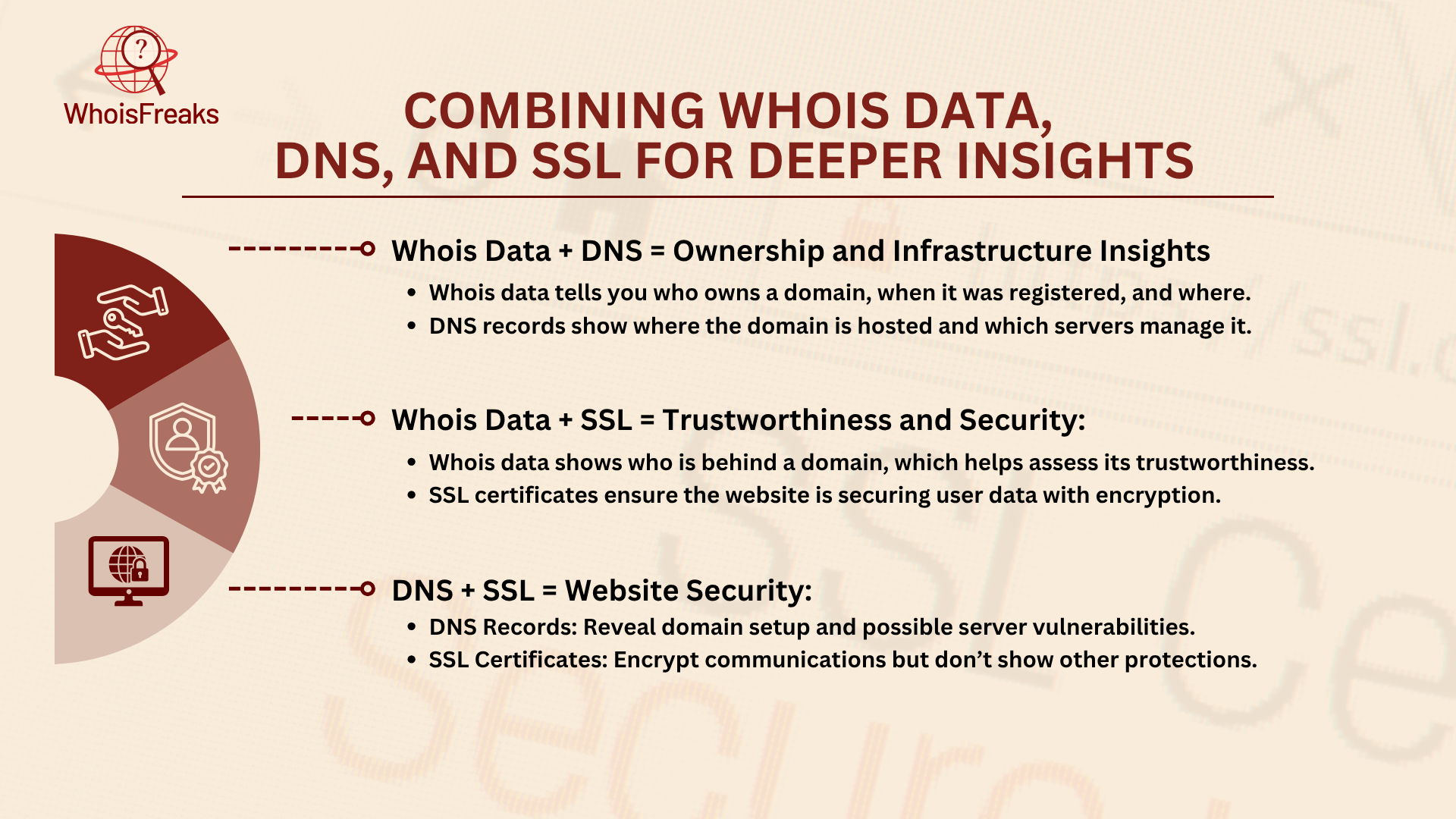
By comparing these two, you can identify discrepancies, such as a domain being owned by one entity but hosted on servers controlled by someone else. This can hint at third-party services or potential security risks from unknown servers.
Together, these datasets can help determine if a website is legitimate. For example, if a domain uses privacy protection for WHOIS data but lacks an SSL certificate, it might indicate a risky or fraudulent site.
By analyzing both, you can better assess website security. If the DNS records point to outdated servers and the SSL certificate is expired or from an unreliable provider, the site could be vulnerable to attacks.
WHOIS data, DNS records, and SSL certificates offer more than just security benefits; they can also provide valuable resources that give businesses a competitive edge. By using these data sources, companies can make smarter decisions, monitor competitors, and discover new opportunities for growth.
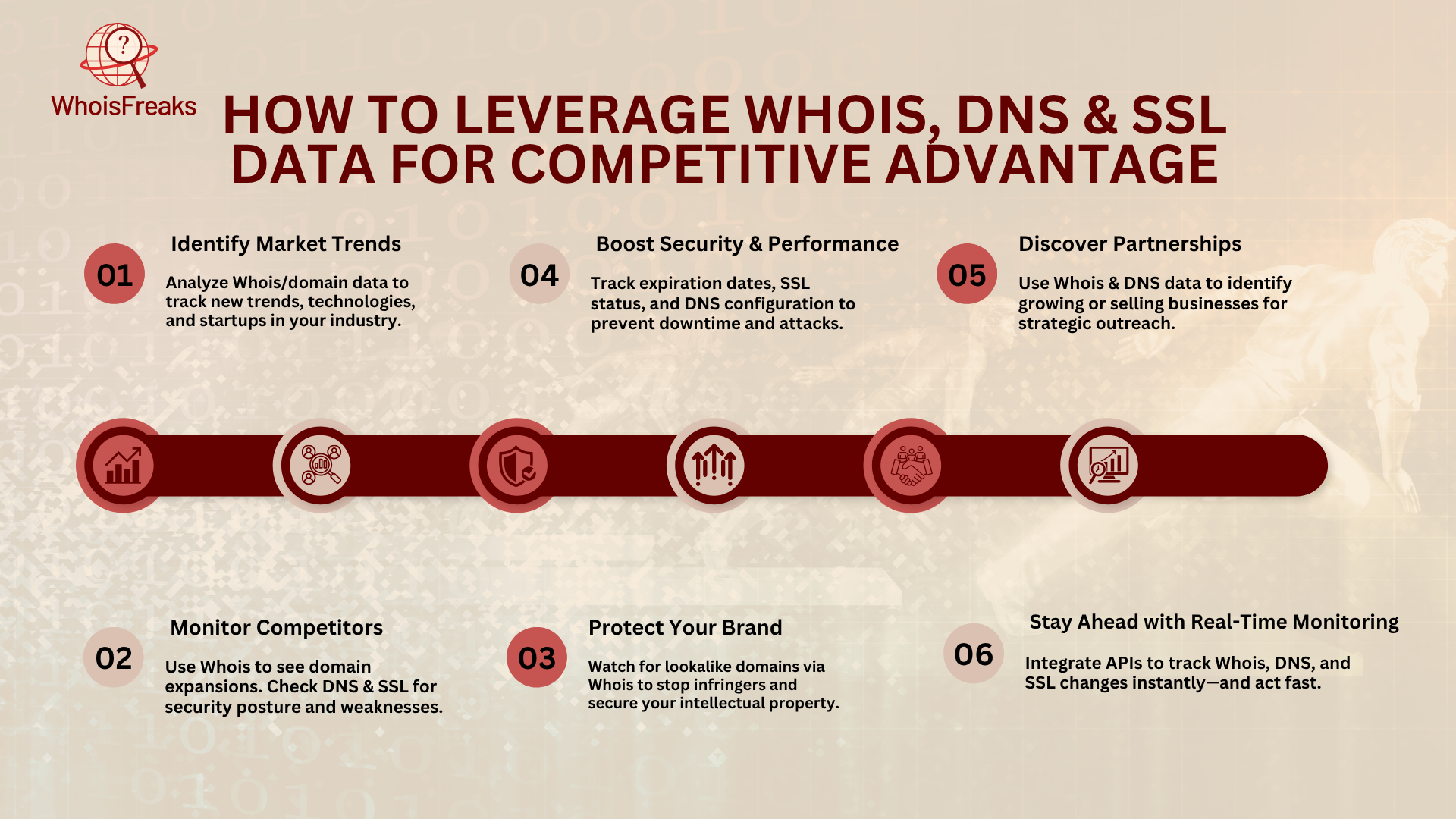
By analyzing WHOIS and domain data, businesses can spot emerging trends and new opportunities. For example, new domains in your industry could signal a shift toward new technologies or services, which you can take advantage of. Monitoring WHOIS records also helps you discover startups entering your niche, giving you a chance to position yourself early or form partnerships. You can even find other domains owned by the same company to learn about their online presence and where you might outperform them.
Tracking competitors' domains, DNS records, and SSL certificates gives you valuable insights into their strategies. WHOIS data can show if they are expanding their digital presence, while DNS and SSL records tell you how secure their websites are. If a competitor's SSL certificate is expired or weak, you can use it as an opportunity to highlight your own stronger security, making your website seem more trustworthy.
Monitoring WHOIS data for domains similar to yours helps protect your brand from potential infringers or domain squatters. If you spot suspicious domain names that are similar to your own, you can act early by purchasing those domains or filing for trademark protection. This helps prevent others from taking advantage of your brand and ensures your intellectual property is secure.
By checking your domain's expiration dates and SSL certificate status regularly, you can avoid interruptions and maintain a secure website. Reviewing DNS records ensures your website is properly configured and safe from attacks. A strong SSL certificate not only secures your site but also boosts your SEO, builds trust with users, and sets you apart from competitors who may neglect these security aspects.
WHOIS and DNS data can help you spot businesses that might be open to partnerships or acquisitions. By checking WHOIS records, you can find companies that are selling domains or expanding their online presence. This gives you an early opportunity to reach out for partnerships or explore acquisitions that can help grow your business.
Real-time monitoring of WHOIS, DNS, and SSL data is key to staying competitive. Using APIs, you can track changes like domain ownership shifts or SSL certificate renewals as they happen. This allows you to quickly react to changes in your competitors' strategies and stay ahead in the market.
To make the most of WHOIS data, DNS records, and SSL certificates, it's crucial to establish a routine monitoring strategy. Regularly reviewing these elements helps keep your domains secure, identify potential threats, and stay ahead of competitors. Here are some best practices to follow:

Setting alerts for domain and SSL certificate expiration dates is key to avoiding downtime and security risks. Use tools like WHOIS lookup services or DNS platforms to get notifications before your domain expires. Similarly, set reminders for SSL renewals at least 30 days ahead to prevent any issues.
Ensure your DNS records are correct and secure to prevent downtime or security breaches. Regularly check your Name Server (NS) and Mail Exchange (MX) records. Make sure your DNS resolution is working as expected and be on the lookout for any unauthorized changes or issues.
Always have a valid SSL certificate to ensure secure connections and improve SEO. Regularly check the expiration date and use tools like SSL Labs to verify the certificate's strength. For high-traffic or e-commerce sites, consider using Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificates for higher trust and security.
Track changes in WHOIS records to spot ownership or registration shifts. Unauthorized changes may signal a cyberattack or security threat. Ensure your domain registrar is reputable and use extra protection features like two-factor authentication and domain locking to safeguard your domain.
Given the volume of data to monitor, automation is essential for your ability to efficiently track changes. Use APIs for continuous DNS and WHOIS record monitoring and get alerts for any critical changes. SSL monitoring tools can also track your certificates and notify you if they're about to expire or need reconfiguration.
Monitor your competitors' WHOIS, DNS, and SSL data, including domains registered, to stay informed on their strategies and security posture. Set up alerts for domain changes, check if their SSL encryption is up to standard, and track their DNS records for any security vulnerabilities. This can give you an edge by identifying their weaknesses.
Stay current with industry changes by following security blogs, subscribing to bulletins, and keeping up with ICANN regulations. Be aware of updates to SSL standards to ensure your website is always meeting the latest security protocols.
In today's interconnected digital world, understanding the relationship between WHOIS data, DNS records, and SSL certificates is essential for anyone looking to secure their online presence and gain valuable insights. Each of these data sets provides unique, actionable information about a website's ownership, infrastructure, security, and potential risks. Individually, they offer key details, but when combined, they provide a much deeper, more comprehensive analysis of a domain's operations.
WHOIS data allows you to learn about a domain's ownership, registration details, and historical data. This information gives your insight into the transparency of a website's origin and current state. DNS records, on the other hand, provide a view of the domain's hosting infrastructure, email systems, and server configurations, which are essential for ensuring a site is running smoothly and securely. Lastly, SSL certificates play a crucial role in encrypting communication, protecting user data, and boosting trust with customers. They are also a key factor in SEO rankings, as websites with SSL certificates are favored by search engines.
When you combine WHOIS, DNS, and SSL data, you unlock a powerful tool for in-depth analysis. This combination allows you to not only enhance your website's security by ensuring all aspects of your domain are configured correctly, but also to monitor your competitors and uncover valuable business insights. By looking at these three datasets together, you can identify potential security risks, monitor for domain hijacking or fraud, and keep an eye on any changes that might impact your operations. This strategic approach to online presence management can help you stay one step ahead in a constantly evolving digital landscape.

Understanding DNS spoofing and how to protect yourself is crucial to keeping your online activities safe. Let’s dive into what DNS spoofing is, how it works?
10 min read

Learn what SSL/TLS certificates are and why they are essential for website security and data protection.
6 min read