
Phishing Prevention Using Subdomain Discovery to Thwart Spoofing Campaigns

By Qasim
Posted on July 22, 2025 | 12 min read


By Qasim
Posted on July 22, 2025 | 12 min read
Phishing attacks are no longer restricted to suspicious emails or obviously fake websites, and they are a normal form of cyber-attack, often perpetrated by malicious actors. Today's attackers take advantage of subdomains which are components of a URL found before the main domain to make a malicious link look like a good link, potentially leading to the theft of sensitive information.
With strategies such as typo squatting, cloud platform abuse, and subdomain impersonation, the threat actors are able to generate URLs that some users will find easy to overlook and even the most simplistic of security barriers, thus increasing the attack surface for these organization. Even worse, quite a number of organizations do not even know that there are so many subdomains within their control, thus leaving loopholes that attackers can use to get hold of sensitive data.
In this blog, we will discuss how subdomains are being used as a phishing weapon in active campaigns in the wild and steps that can be taken to counter subdomain-based spoofing attacks and enhance the defense against phishing campaigns, including measures against credential harvesting.
One of the most widespread and dangerous cyber threats nowadays is phishing. It normally consists of fraudulent emails or messages who redirects the recipient to malicious websites which are maliciously programmed to steal data, including logins, financial information, or intellectual property. They may be a part of campaigns that target large groups of people or small and specific spear phishing attacks that impersonate trusted brands or employees.
In order to protect against phishing, an organization needs to have insight into its own digital infrastructure, even the subdomains. Phishers commonly rely on abandoned, incorrectly set up, or weak subdomains to serve phishing web pages or impersonate genuine applications. It is at this point where a subdomain enumeration tools like WhoisFreaks Subdomains Lookup, DNS Lookup, CNAME records, and Historical DNS Lookup become important tools that identify and keep a watchful eye on these possible weak points.
In 2017, a subdomain takeover vulnerability was identified in Uber's infrastructure. Security researcher Avinash Jain discovered that an abandoned subdomain (surveys.uber.com) was still pointing to a third-party service no longer in use. This misconfiguration left the subdomain vulnerable to takeover, meaning an attacker could have hosted a phishing page under Uber's legitimate domain. Such an attack would likely appear trustworthy to users, increasing the chances of credential theft or data compromise.
Read more about phishing here: Understanding Phishing Attack: Techniques and Prevention Tips
Domain spoofing refers to the situation in which cybercriminals use a spoofed domain name or email address to attempt to deceive users. Domain spoofing aims to get a user to engage with a fake email or a phishing site that is designed to be mistaken by the user to be genuine. Domain spoofing is simply an imposter who presents bogus proofs to a person in order to win their trust then proceeds to exploit the person.
Subdomain spoofing is a less public way of domain spoofing. Criminals are taking the subdomains and copying them to look like genuine sites, often to launch a phishing attack. As an example, login.paypal.com.fakewebsite.com would be a dangerous link. In this case, the root domain (paypal.com) has been disguised by a malicious root domain (fakewebsite.com). Also, given the tendency of people to quickly scan URLs, such structure may fool human users to think that they are actually on a harmless reliable site. In a more severe form, the phishing pages are hosted on the abandoned or misconfigured subdomains which in fact represent some real organizations, making it even more difficult to detect.
Subdomain discovery is the process of finding all the subdomains that belong to a domain in order to find any concealed parts of the property, overlooked infrastructure, or a possible weak point of attack. It is a vital practice of decreasing an attack space and managing a range of vulnerabilities and security threats, particularly when speaking of preventing phishing.
WhoisFreaks supports this process through its Subdomains Lookup Tool, which provides structured data on known subdomains for any queried domain. Unlike brute-force or active scanning methods, WhoisFreaks leverages passive DNS data and historical records to identify subdomains efficiently and non-intrusively, minimizing the risk of alerting or overloading target infrastructure.
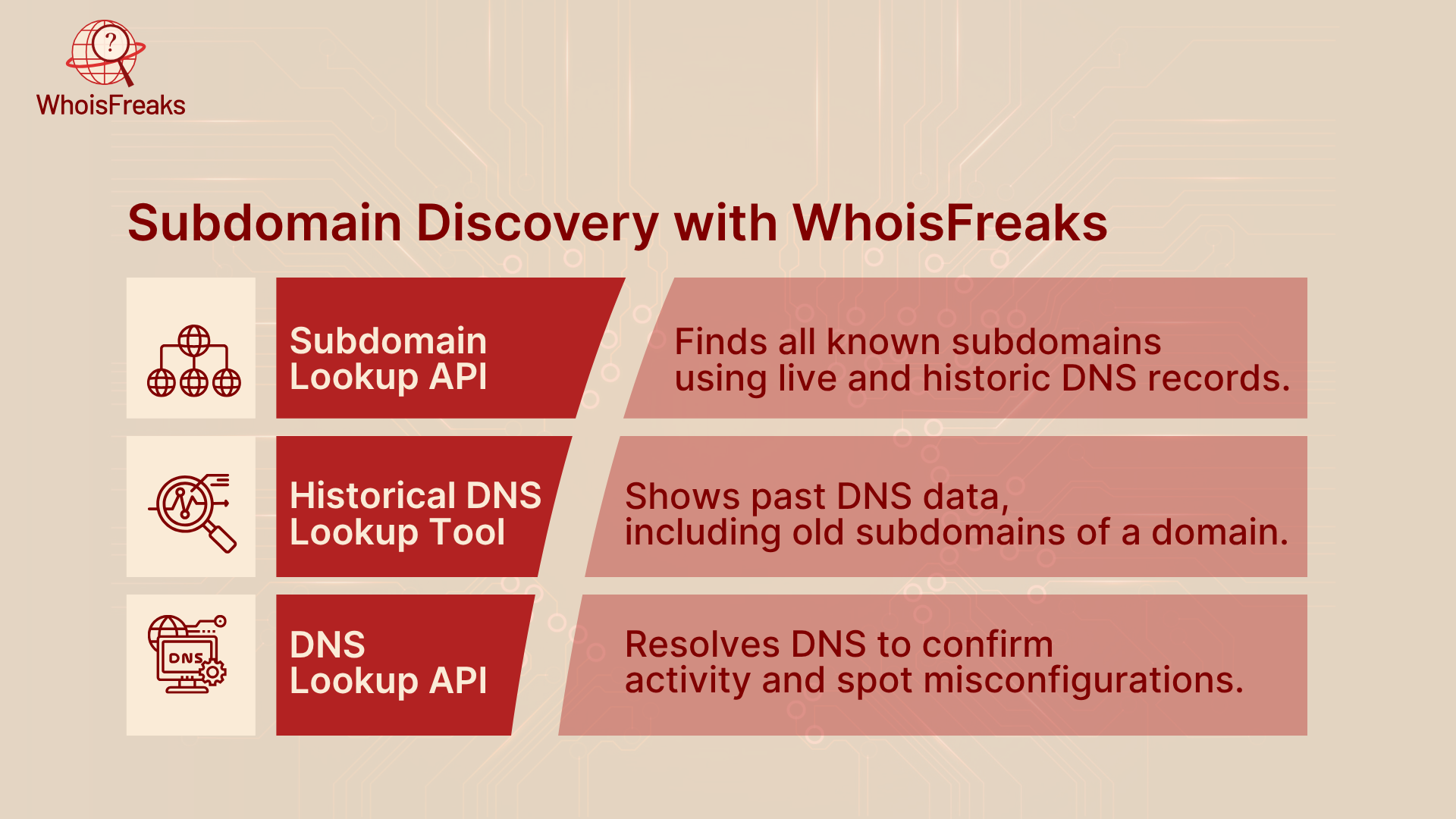
Subdomain discovery plays a critical role in detecting phishing campaigns before they reach users. Here’s how:

Subdomain discovery is only valuable if it’s actively integrated into your broader cybersecurity workflow. It’s not just about finding subdomains, it's about continuously monitoring, analyzing, and responding to what you uncover. This section outlines how to operationalize subdomain discovery and the use of a subdomain enumeration tool as part of your phishing and spoofing defense strategy.

Preventing phishing isn’t just about blocking emails or spotting suspicious links it requires a multi-layered security strategy that combines visibility, policy, and proactive defense. One of the most overlooked layers is the subdomain level, where attackers often find hidden entry points for financial gain .

WhoisFreaks enables organizations to build a stronger phishing defense by offering tools that support continuous discovery and monitoring:
In parallel, organizations should implement email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent domain spoofing through fake email headers. Lastly, security awareness training for employees remains a critical layer empowering users to recognize and report phishing attempts before they cause damage.
Let’s walk through an example of how a security team can use WhoisFreaks' API tools to detect and prevent a phishing attack that’s hiding behind a suspicious subdomain.
A mid-sized tech company’s IT team notices a few employees reporting phishing emails. The emails contain a login link that appears to be internal something like auth-login.screenshotapi.net.
At first glance, it looks legitimate, but the team has no record of this subdomain ever being created.
The security team uses WhoisFreaks Subdomains Lookup tool to get a full list of discovered subdomains for their main domain:
GET https://api.whoisfreaks.com/v1.0/subdomains?apiKey=API_KEY&domain=screenshotapi.netThis confirms that the suspicious subdomain is active and has a DNS history.
Using WhoisFreaks' DNS Lookup API, they check where auth-login.screenshotapi.net is pointing.
The DNS response shows it’s resolving to a public IP hosted on a cloud provider not used by the company.
To dig deeper, they call the Historical DNS Lookup Tool and discover:
The team quickly flags the subdomain as malicious and initiates takedown procedures. They also block the IP and domain internally using their firewall and email filtering systems.
An alert is pushed to the company’s SIEM platform, and IT updates internal documentation to ensure no similar misconfigurations go unnoticed.
Phishing attacks can escalate quickly, especially when targeting critical infrastructure, government systems, or high-value organizations. Such attacks can lead to valuable assets outages, data breaches, and significant reputational harm.
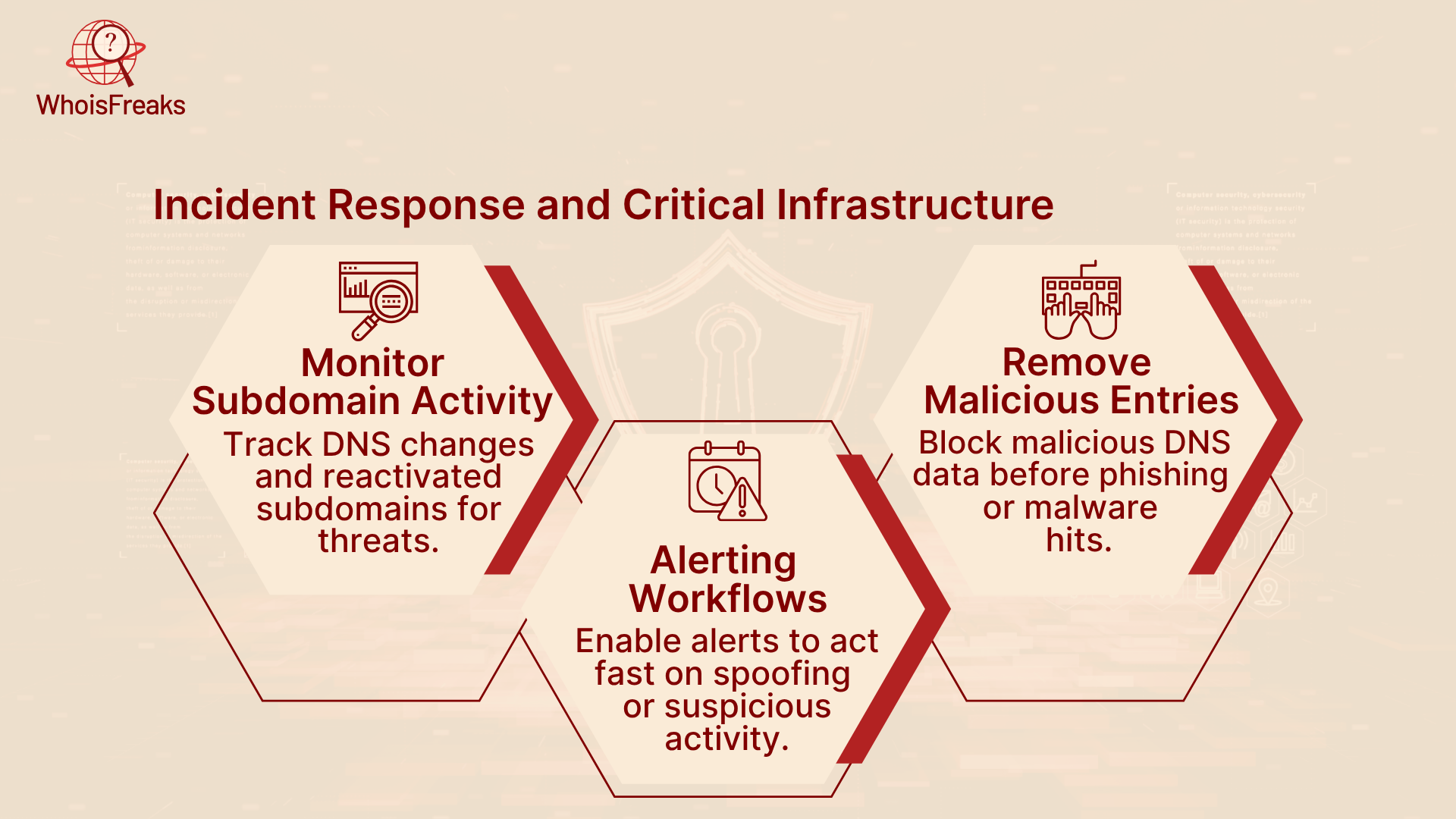
An effective incident response plan should be tightly integrated with domain monitoring processes. Using WhoisFreaks' toolset, security teams can:
Maintaining accurate visibility over your domain structure ensures that your team is not only alerted to threats but also equipped to act fast reducing response times and minimizing exposure.
Subdomain management is a very important part of modern cyber security management especially as it pertains to the protection against phishing and spoofing attacks that can compromise sensitive data. Due to the ease of neglecting or misconfiguration subdomains, they usually serve as a sweet spot to attackers interested in impersonating brands, such as software vendors, through payload phishing or exploiting forgotten infrastructure.
The first and the most significant best practice is to have proper inventory with all the subdomains that are associated with your organization domains. This includes the constant utilization of such tools as the Subdomains Lookup Tool by WhoisFreaks to track both the present and historical subdomains, thereby improving security across the organization . Hypervisors with no view into your entire subdomain environment can barely track unauthorized or ill-intentioned use by individual users.
Maintaining DNS hygiene is important along with inventory management. Companies ought to do a review and purge DNS records regularly eliminating subdomains in use, or those pointing at services that are no longer current. Badly set up or unused DNS entries may leave systems vulnerable to takeover, particularly when they are connected to past-due third-party platforms.
Use of powerful DNS and email security enhancements also enhance your security. Authentication mechanisms such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC can be used to verify that only allowed servers can be used to send email on your behalf, preventing malicious messages purporting to be from your domain or subdomain that are containing malicious code . On the same note, implementing DNSSEC would counteract the alteration of DNS records by digitally signing DNS information to verify its integrity.
Finally, DNS configurations and access should be on a principle of least privilege. DNS settings should only be modified by authorized and all modifications must be audited and logged. Poorly defined access or change control processes may result in unwitting misconfigurations or unrecognized openings.
While subdomain discovery is a powerful technique for preventing phishing and spoofing attacks, it is not without its challenges. Organizations must be aware of the limitations and complexities involved, especially when preparing for a targeted attack, to effectively integrate it into their security strategies that can evade detection.

Sophisticated threat actors tend to apply methods aimed at escaping detection systems. One such technique is fast-flux DNS, which is when IP addresses related to a domain switch quickly, and it is harder to block or follow the malicious infrastructure. Likewise, wildcard domains (e.g. *.maliciousdomain.com) enable attackers to create thousands of unique subdomains in a matter of seconds, and prevent discovery tools and filters. Such evasive strategies decrease the effectiveness and visibility of conventional monitoring.
Passive DNS based approaches to traditionally only use subdomain discovery tools, and as such may present an incomplete view. These data are reliant on publicly posted DNS records, cert transparency logs, and third parties. Therefore, subdomains that have never been registered publicly, newly created, or are closed internally (to firewalls or authentication) might not be present in those datasets. That is not all, since even the most comprehensive passive discovery tools might fail to detect important aspects of the digital fingerprint of an organization.
It will be necessary to maintain a stable amount of subdomain discovery and monitoring, both in terms of the technical resource and the human resource. Teams have both to deploy and pave the way to scheduled scans, the historic merge of outcomes into SIEM or threat detection systems, and the exploration of warnings as they do. This degree of constant supervision might prove challenging to maintain in organizations that have small budgets or teams where there is a lack of automation or security infrastructure. Consequently, there is a possibility of unidentified or uncured threats.
Phishing remains one of the most successful cyberattacking techniques yet it is one of the most avoidable. When organizations prioritize their visibility, hygiene, and layered defense, they may remain safe from phishing emails and other cyber threats . This visibility lies in subdomain discovery, which is essential for preventing any potential cyber-attack . It assists security teams to discover, track, and control the regions that are typically neglected: subdomains that are at risk of spoofing, hijacking or misuse.
WhoisFreaks has very potent mechanisms that can enable vendors to initiate vulnerability exploration efforts, domain change tracking and potential impersonation guard at the infrastructure level.
Through robust DNS standards, automation of security, and end-user education this level creates a potent phishing and spoofing barrier defense. In this day and age, it is no longer a choice to be able to be aware of what is beneath your domain: it is a security necessity.
Explore WhoisFreaks suite of tools to start strengthening your phishing defenses today.

Historical WHOIS data is the digital fingerprint of domain activity. WhoisFreaks tools help security teams trace attackers, rebuild attack timelines, preserve court-ready evidence, and detect threats early, strengthening incident response and proactive cybersecurity defenses.
10 min read

Explore how WHOIS history aids forensic analysis in cybercrime investigations. Learn effective strategies to enhance your cyber defense. Read more now!
9 min read