

By Qasim
Posted on June 03, 2025 | 10 min read
A strong email reputation is key to success in email campaigns and marketing. Your DNS setup and DNS records must be correct to avoid common DNS vulnerabilities. DNS, or Domain Name System, works like the internet’s phonebook. It turns domain names into IP addresses and handles DNS responses. Good DNS configurations help with email authentication and sender verification.
If DNS misconfigurations happen, your email can face big risks. Problems like phishing attacks and domain spoofing can harm your email security and domain reputation. When DNS verification fails, your emails may end up in spam or get rejected. This hurts your brand credibility and lowers email trust with your recipients. Email filtering relies on message authenticity, which comes from solid DNS records and domain spoofing protection.
In today’s digital world, email safety is very important. Right DNS settings boost email reliability and stop email reputation damage. This helps your emails reach the inbox every time, especially when you manage zone transfers properly. By fixing DNS issues, you keep your email systems safe and protect your email reputation. This keeps your messages flowing and your brand strong. In this blog, we will explore the top 5 DNS misconfigurations that could be damaging your email reputation and how to fix them.
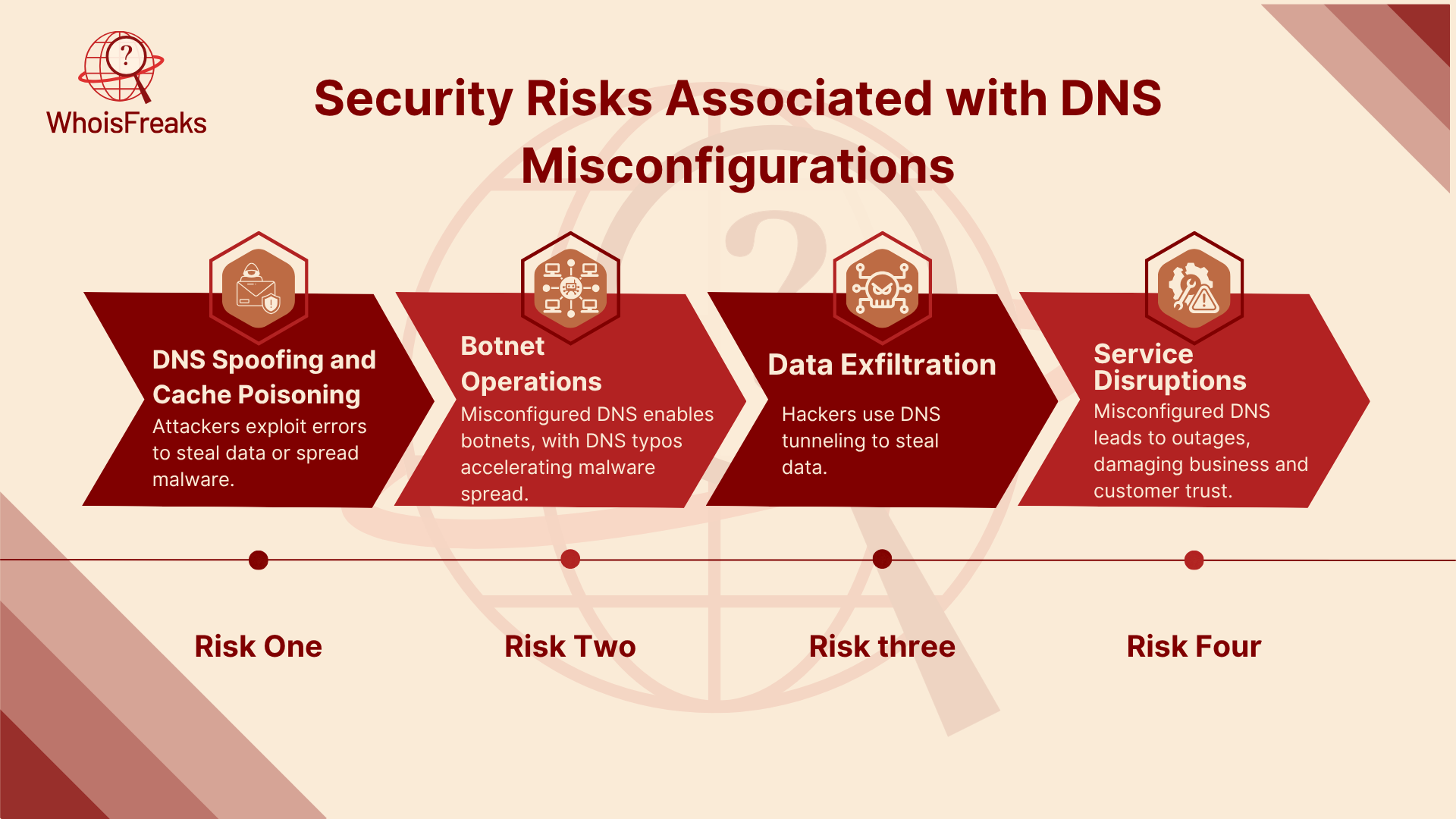
When did you last check your DNS settings? For many groups, DNS is a key part of their system. It works quietly, turning domain names into IP addresses to keep things running well. But DNS misconfigurations can let attackers in, leading to a DNS attack. This causes big problems for security teams, like data leaks, downtime, exploits, and DNS poisoning.
Recent reports show how big this problem is: 72% of groups had a DNS attack last year. Almost half of these were DNS hijacking, where bad actors change DNS queries to send users to harmful servers. Also, more than 4% of domains using DNSSEC had serious misconfigurations. Many of these failed to resolve DNS correctly.

Because of these risks, security pros and researchers have a big job. They must find and fix DNS misconfigurations early. Doing this helps make defenses stronger and cuts down on risks, including serious security risks. This keeps the digital world safer for everyone.
The domain name system (DNS) is like the internet’s phonebook. It changes easy-to-read domain names like yourcompany.com into IP addresses that computers use to talk to each other. But DNS does more than just guide web traffic—it also helps with email delivery and keeps your emails safe.
There are some key DNS records that help make sure your emails are trusted and sent the right way. These include:
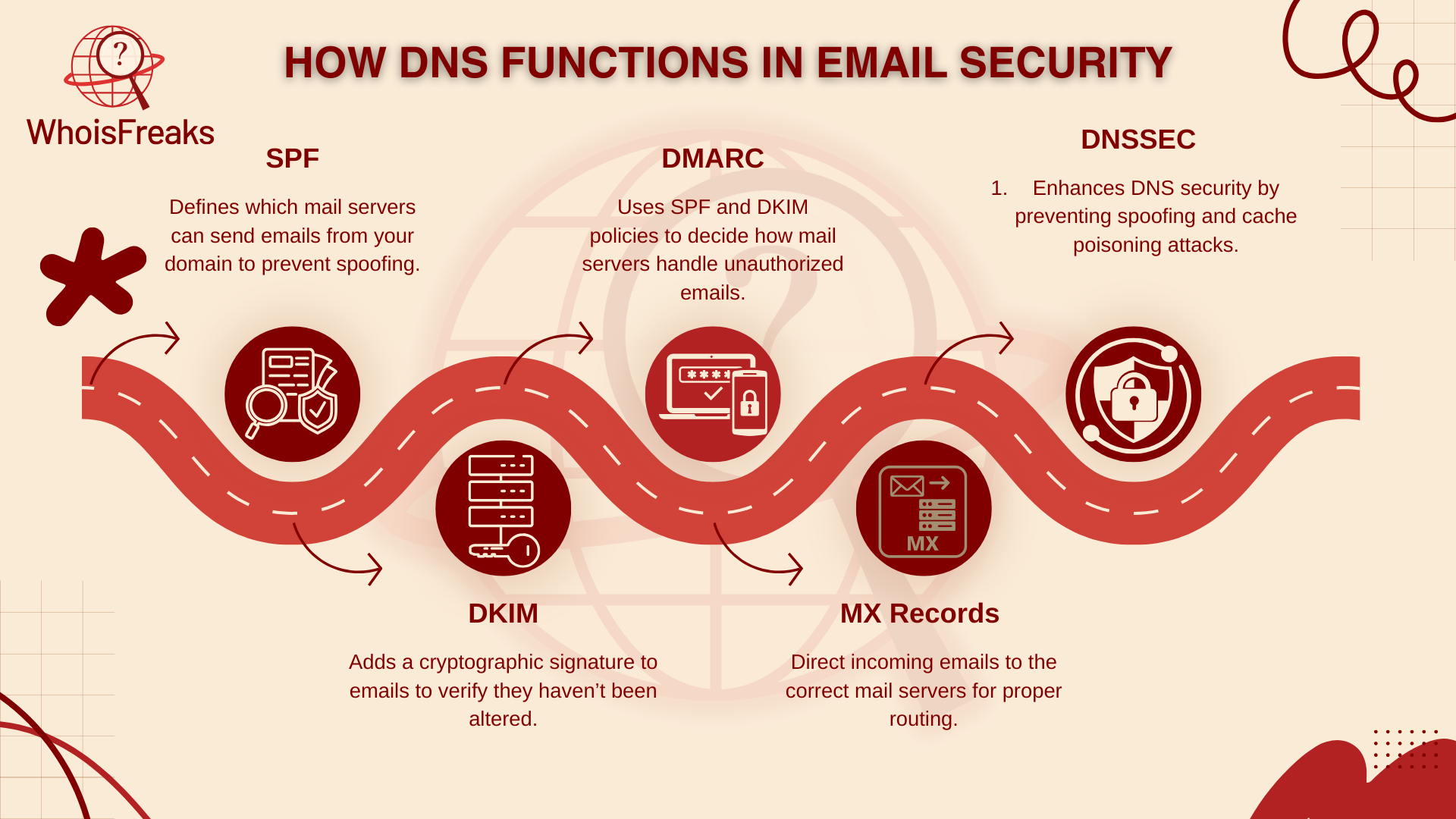
When these DNS records are set up right, mail servers can check that your emails really come from you. This cuts down the chance of your emails ending up as spam or getting rejected. But if these records are missing or incorrect DNS records, your domain can be open to spoofing, phishing, and delivery problems—things that hurt your email reputation.
DNS misconfigurations are more than just a pain. They can let in big security threats, such as:
Sender Policy Framework, or SPF, is a type of DNS record that works like a guest list for your domain. It tells mail servers which senders are allowed to send emails on your behalf. When SPF is set up correctly, it helps receiving servers check if your emails are real and safe.
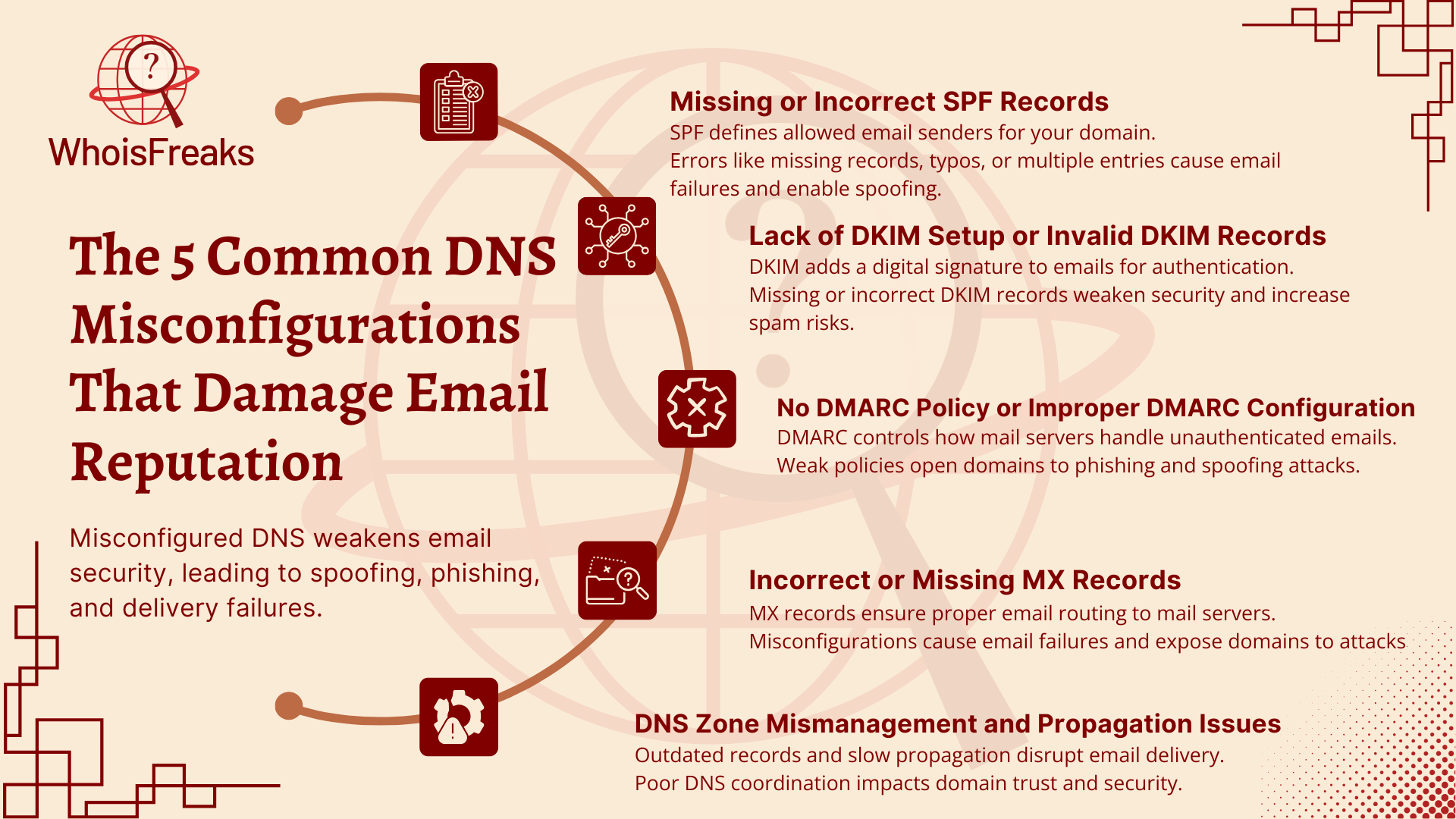
Without a proper SPF record, spammers can pretend to be you. This makes it more likely your emails will be marked as spam or bounced back due to DNS hijacking.
DomainKeys Identified Mail, or DKIM, adds a digital signature to your emails. This signature proves the email has not been changed during transit and really comes from your domain.
If DKIM is missing or invalid, mail servers may doubt your emails’ authenticity. This increases the chance your messages get flagged as spam or rejected. Setting up DKIM correctly helps keep your emails safe and builds trust in your domain.
DMARC, which stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, works with SPF and DKIM. It lets domain owners' control how receiving servers handle emails from their domain.
Without a good DMARC policy, your domain is open to phishing and spoofing attacks. These attacks can harm your brand’s reputation and cause email delivery problems. A well-set DMARC policy not only protects your domain but also provides reports to help you track email activity.
Mail Exchange, or MX, records tell the internet where to send incoming emails for your domain. Managing these records correctly and ensuring they are properly configured is key to security and smooth email delivery.
Misconfigured MX records can lead to email delivery failures and leave your domain open to spoofing attacks. Keeping your MX records accurate and free from stale DNS records is crucial for reliable email communication and a good email reputation.
Your DNS zone file contains all the DNS records for your domain. This includes records important for email delivery and security, such as those used in DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions). Poor management of your DNS zone like leaving outdated records, causing conflicts, or slow propagation of changes can cause serious email problems.
These problems can lead to mail servers rejecting your emails or marking them as suspicious. This harms your sender reputation and can disrupt your email flow. Keeping your DNS zone clean and updated on time helps keep your email system safe, secure, and reliable.
By carefully managing these five common DNS misconfigurations, you ensure your emails reach the inbox and build a strong, trusted email reputation for your domain.
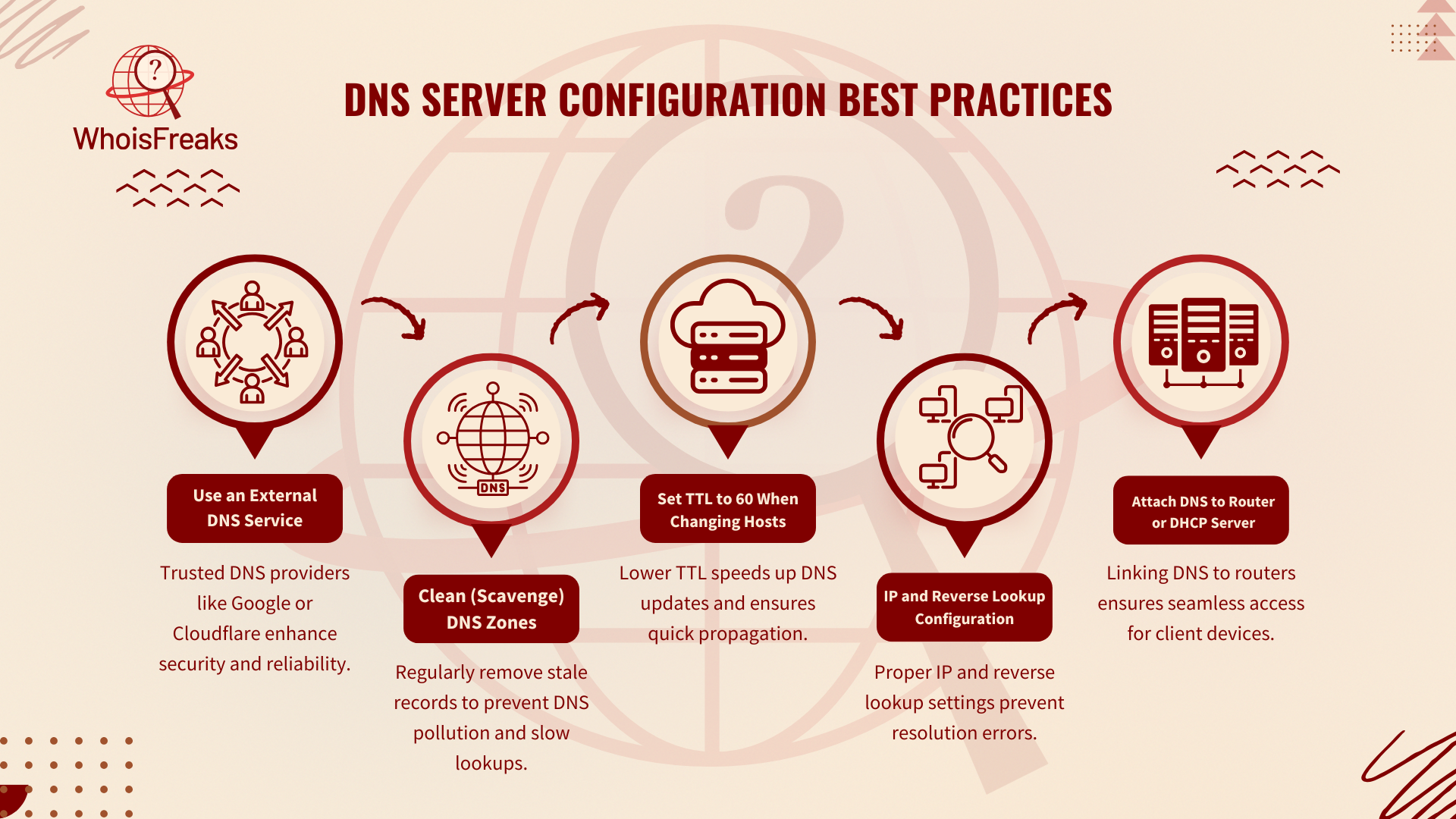
Setting up a DNS server takes good planning and care to work well, stay safe, and be reliable. Here are some best tips to follow:
Other DNS risks, such as those posed by a malicious server, can hurt your email security and good name, beyond key records like SPF, DKIM, DMARC, MX, and DNSSEC.

These servers answer DNS queries from any IP. Hackers can misuse them in DNS amplification attacks, flooding targets with traffic. This can get your domain or IP blacklisted and hurt your email reputation.
These let all subdomains point to one IP or service. While handy, they risk subdomain hijacking, where bad actors make fake subdomains under your domain. This can dodge email filters or start phishing attacks.
TTL shows how long DNS records stay cached. If TTL is too long, changes to important DNS records like SPF or MX take longer to update, causing email checks to fail. If TTL is too short, it ups DNS traffic and may cause issues.
Sharing too much info in TXT records like internal IPs or server details can help hackers plan attacks. This hurts your domain’s reputation and weakens email security.
Keeping an eye on these DNS issues helps keep your email safe and your domain strong.
Detecting and fixing DNS misconfigurations is key to protecting your email reputation. Here’s how you can audit and improve your DNS setup:
By proactively managing your DNS configuration, you’ll improve email deliverability and address potential deliverability issues while safeguarding your domain’s reputation.
Your domain’s DNS setup is key to keeping your email reputation safe. It helps your emails reach inboxes, not spam folders. Mistakes in SPF, DKIM, DMARC, MX, and DNSSEC records can cause poor email delivery, more phishing risks, and hurt your brand.
Check and fix these DNS settings often. This keeps your domain safe from misuse and builds trust with your customers and email providers. Using best practices like DNS validation, watching DMARC reports, and enabling DNSSEC makes your email more secure and reliable.
Don’t wait for problems to happen. Start today by reviewing your DNS setup. Use the right tools and get expert help if needed. Keeping your domain’s email system strong is key for your email reputation.

Discover essential insights on DNS poisoning and learn practical steps to safeguard your online presence. Read the article for vital protection tips.
10 min read

Learn how a DNS flooder can threaten your network security and discover practical measures to protect your systems. Read more to safeguard your network.
10 min read

Discover the essential role of DNS servers in internet functionality and learn how they enhance your online experience. Read the article for insights.
9 min read