
Essential Introduction to IP Geolocation and Its Security Applications

By Qasim
Posted on August 18, 2025 | 11 min read


By Qasim
Posted on August 18, 2025 | 11 min read
Have you ever gone onto a web site and found that the prices are automatically displayed in your native currency, or it knew which country you were in without providing it with any information? No, it is not a magic, this is IP geolocation in its action, and it draws upon IP geolocation data.
Its technology to identify websites and web-based services to determine the location of a user based on the IP address is called IP geolocation. This geographical information which is facilitated by the geolocation technology assists business to tailor content, anti-fraud prevention and improved security.
In this blog, we’ll explore what IP geolocation is, how it works, and most importantly how it plays a vital role in cybersecurity.
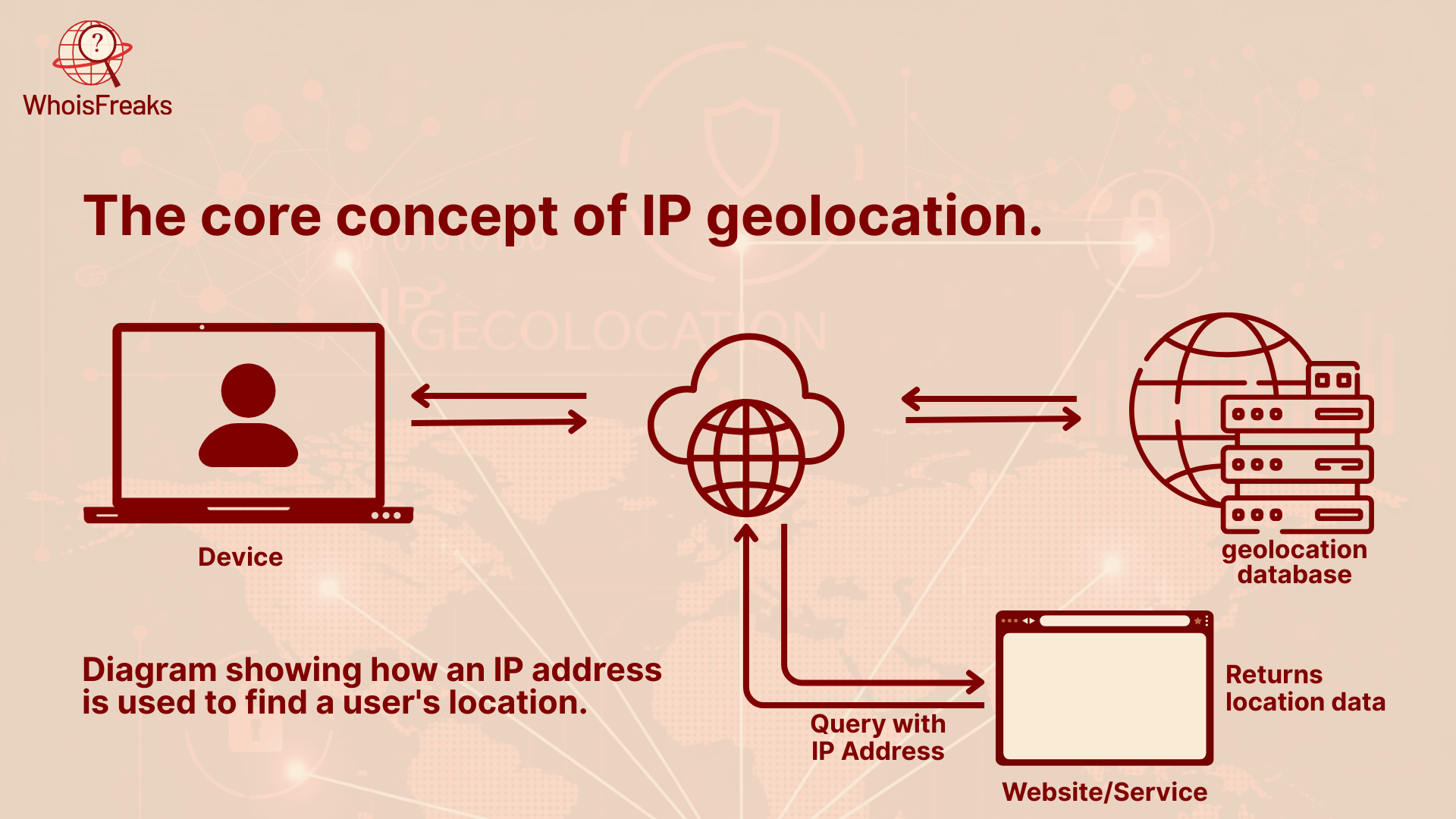
IP Geolocation is a term used to describe the process of locating geographical area of a user based on their IP address. IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique figure that is issued to each device that is connected to the internet just as a home address would be issued to households digitally.
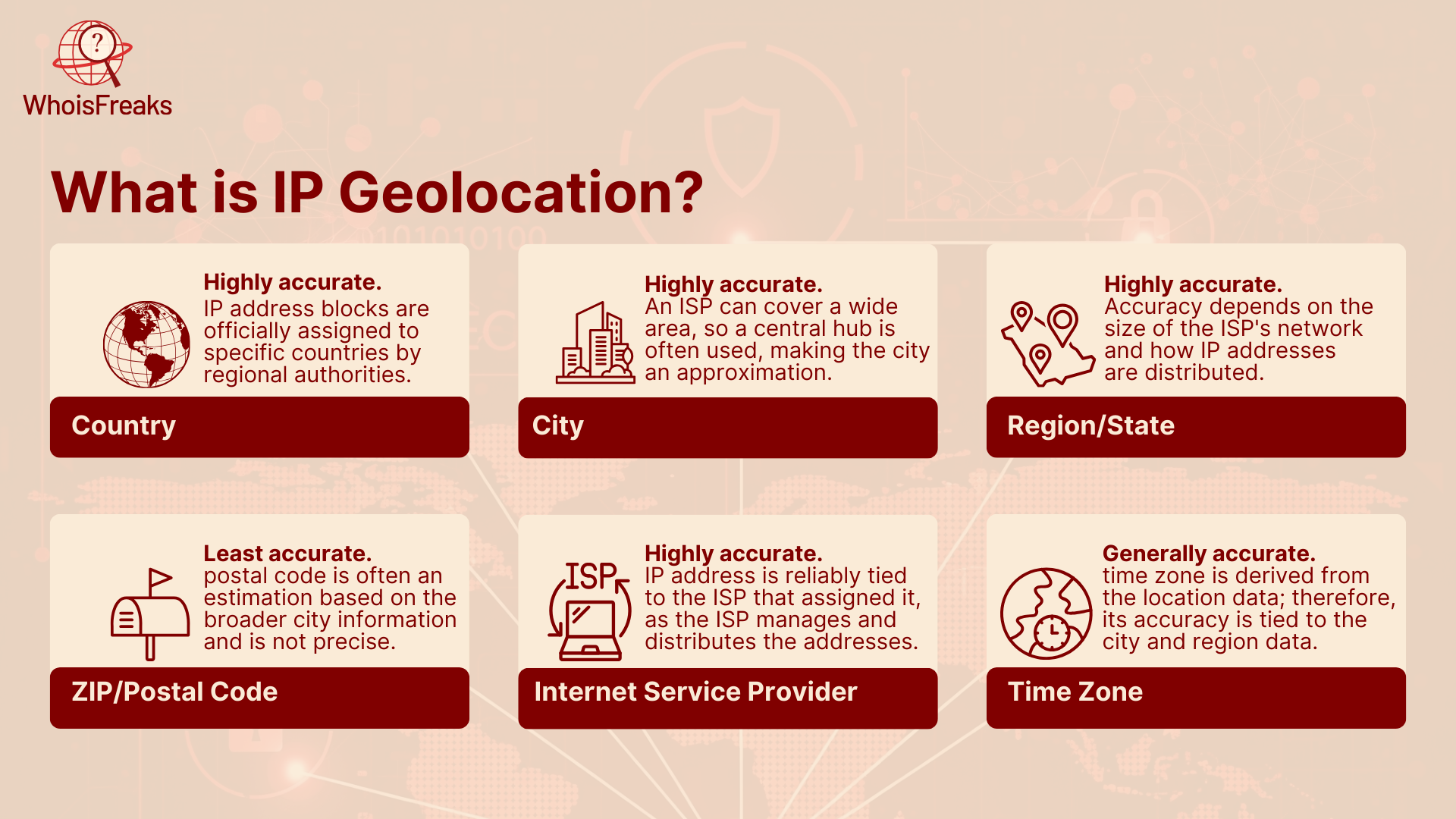
By looking at this IP address, systems can estimate where the device is located. This usually includes:
It’s important to understand that IP geolocation does not provide your precise home address and your unique identity. It provides a rough location information of you, often to city or town, which is served by geolocation services.
Websites and apps widely use this information to improve the user experience, prevent a possible attack or provide geographically tailored contents.
IP geolocation works by using large databases that link IP addresses to real-world locations. When you visit a website, your IP address is checked against one of these databases to estimate where you are using geolocation databases .
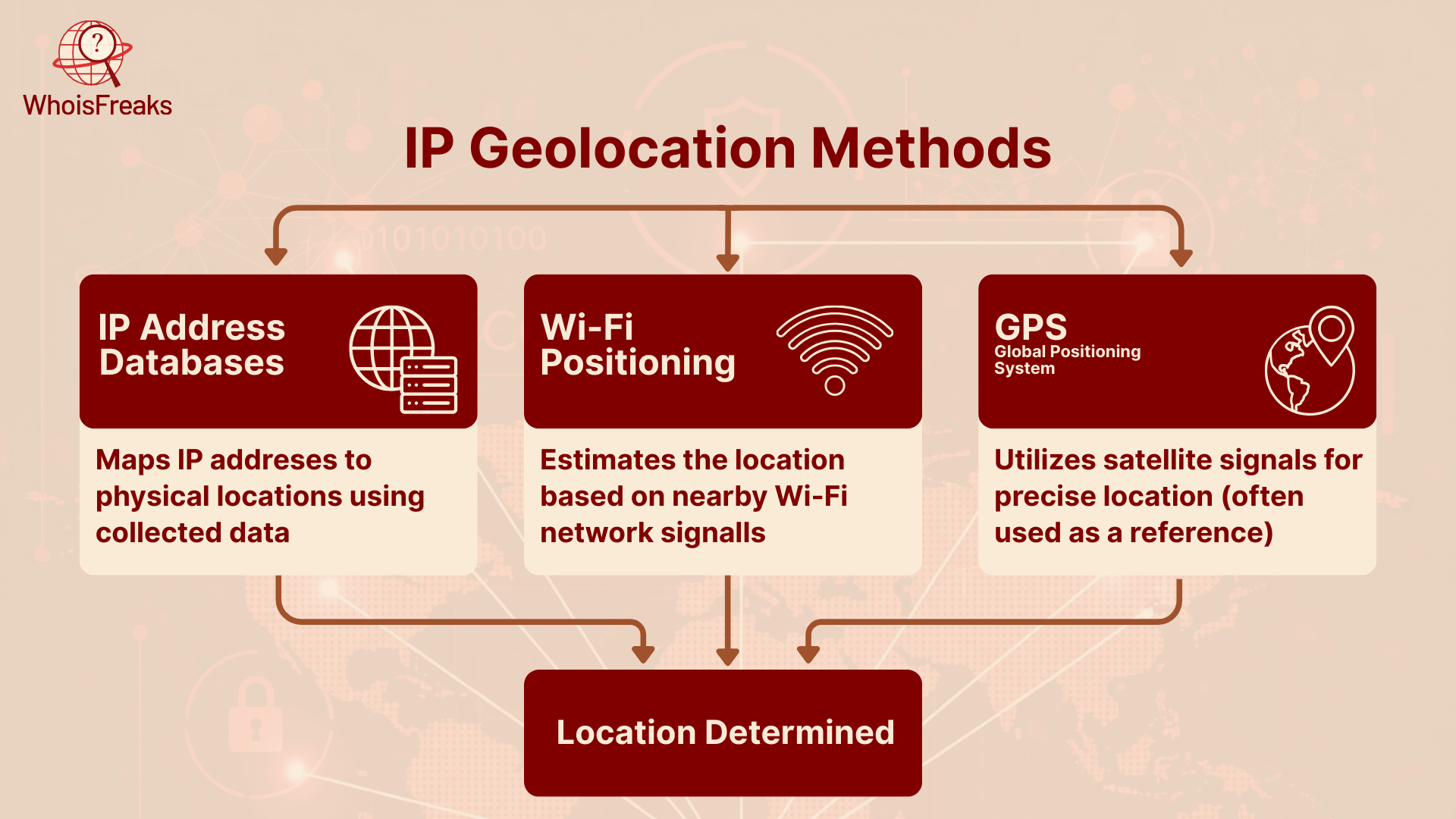
Companies maintain these and update them on a regular basis. They gather information of internet service providers, local internet destination and user machines. When your IP is queried the data base will provide a rough location according to historical information.
When you use Wi-Fi, your device can be tracked down by the local Wi-Fi signals, particularly in cases where GPS is not concerned. This process is common within mobile applications and is more accurate in cities.
While not directly related to IP geolocation, some services combine IP data with GPS for even more precise results especially for mobile apps or navigation tools.
In short, IP geolocation is not 100% perfect, but it's very useful for estimating a general location quickly and automatically. You can use services like WhoisFreaks' Geolocation API that allow developers to access real-time IP data with just a simple API call.
Geolocation of IP addresses is not all about knowing where someone is it is very influential in the way site, applications, and companies relate to users. It has numerous applications in everyday life, including personalizing and stopping fraud.

Let’s break down some of the most common use cases in simple terms:
Have you ever opened a website and noticed that it automatically shows the prices in your local currency or displays text in your language? That’s IP geolocation in action.
This improves user experience without needing you to manually select your country or city.
E-commerce platforms rely heavily on IP geolocation for both customer convenience and security.
This helps reduce fraud and build trust with customers.
IP geolocation also controls what media you can or can’t see based on your region.
This is called geo-blocking, and it’s widely used in digital media services.
Marketers use your IP location to show ads that are more relevant to your area.
This improves ad effectiveness and ensures you see offers that actually matter to you.
In some cases, companies are legally required to treat users differently depending on where they are.
Geolocation helps companies automatically detect user regions and apply the correct legal policies.
Even travel sites use IP geolocation to:
Although IP geolocation is widely accepted as a method of enhancement of user experience, it is also applicable in protecting against cyber-attacks. Information about the origin of traffic will help security teams know when unusual activities are being carried out to help curb attacks and save the sensitive information.
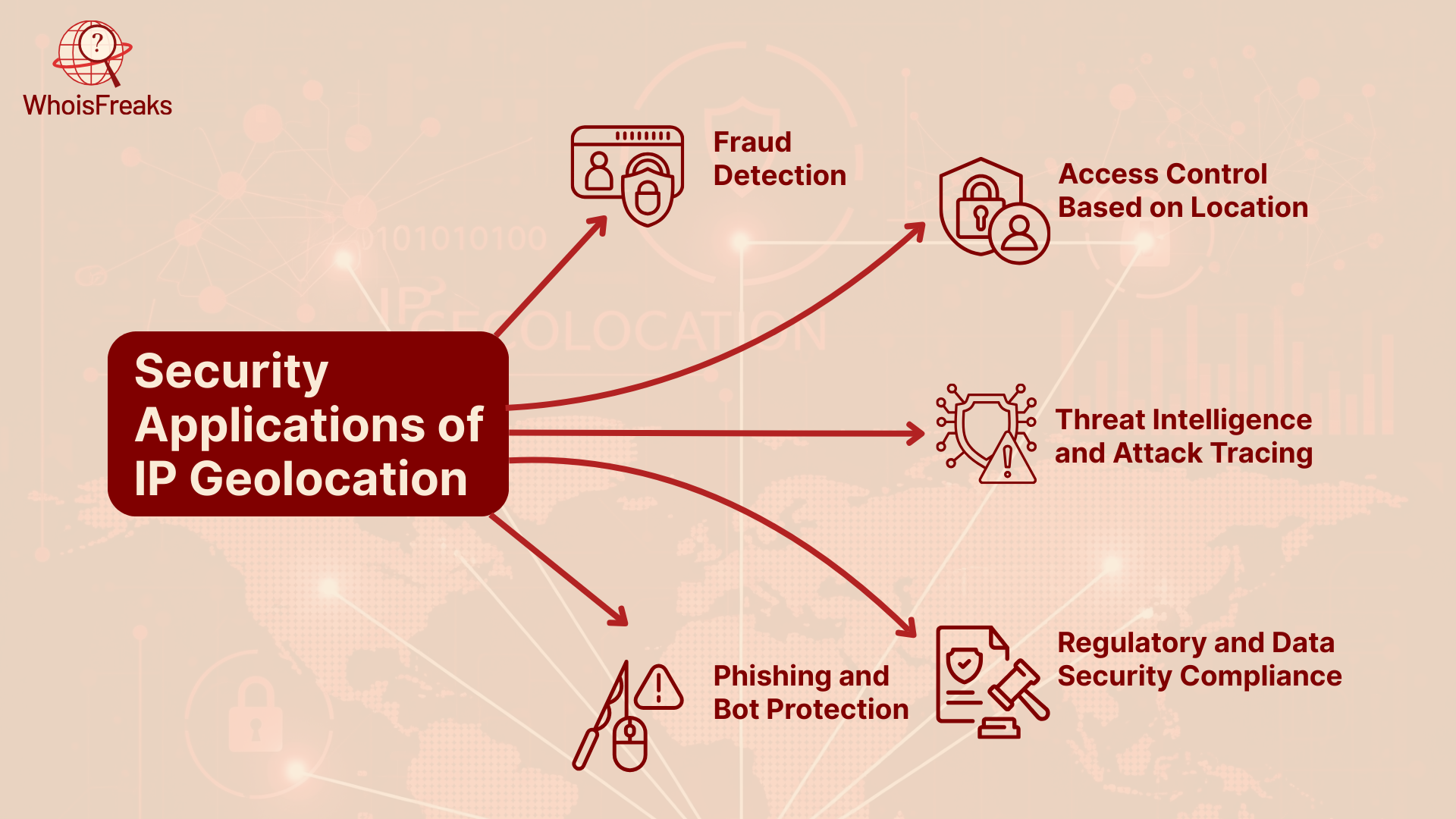
Let’s go through some of the most important security applications:
Imagine you always log into your online bank account from Lahore, Pakistan. One day, someone tries to access your account from Nigeria or the United States within minutes. That’s a red flag.
This helps stop account takeovers, identity theft, and online fraud by monitoring for suspicious activity . APIs like WhoisFreaks are commonly used to detect login anomalies or serve region-specific content.
Businesses require to deny access to various systems or data by location of the user. The best solution to this problem is IP geolocation because it can either accept or reject based on the location of a request.
This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and insider threats.
When a cyberattack happens, knowing the source IP’s location helps security teams trace:
This is useful for incident response, forensics, and threat intelligence gathering.
IP geolocation helps protect against:
For example, if a login bot tries to access accounts from hundreds of IPs across multiple countries in seconds, the system can flag or block them automatically.
Numerous security policies dictate that companies should retain their information in some regions or countries. Because companies can know where users are sourced, they can:
WhoisFreaks also provides a set of tools of which its IP Geolocation API is powerful to use, but all of these are highly useful to every person who might be interested in cybersecurity, development, and digital investigation. These tools aid anything between detecting suspicious IP addresses to tracking the changes of domain names, which makes them the ideal complement to your policies based on geolocation-based security measures.

Here’s a look at the most relevant tools and how they can help:
For quick lookups without coding, this free tool allows you to enter any IP address and instantly get:
Want to know who owns an IP address? This tool shows:
This tool checks whether an IP address is:
Cybercriminals often hide phishing pages or admin portals on subdomains. This tool helps you:
These tools let you track how a domain:
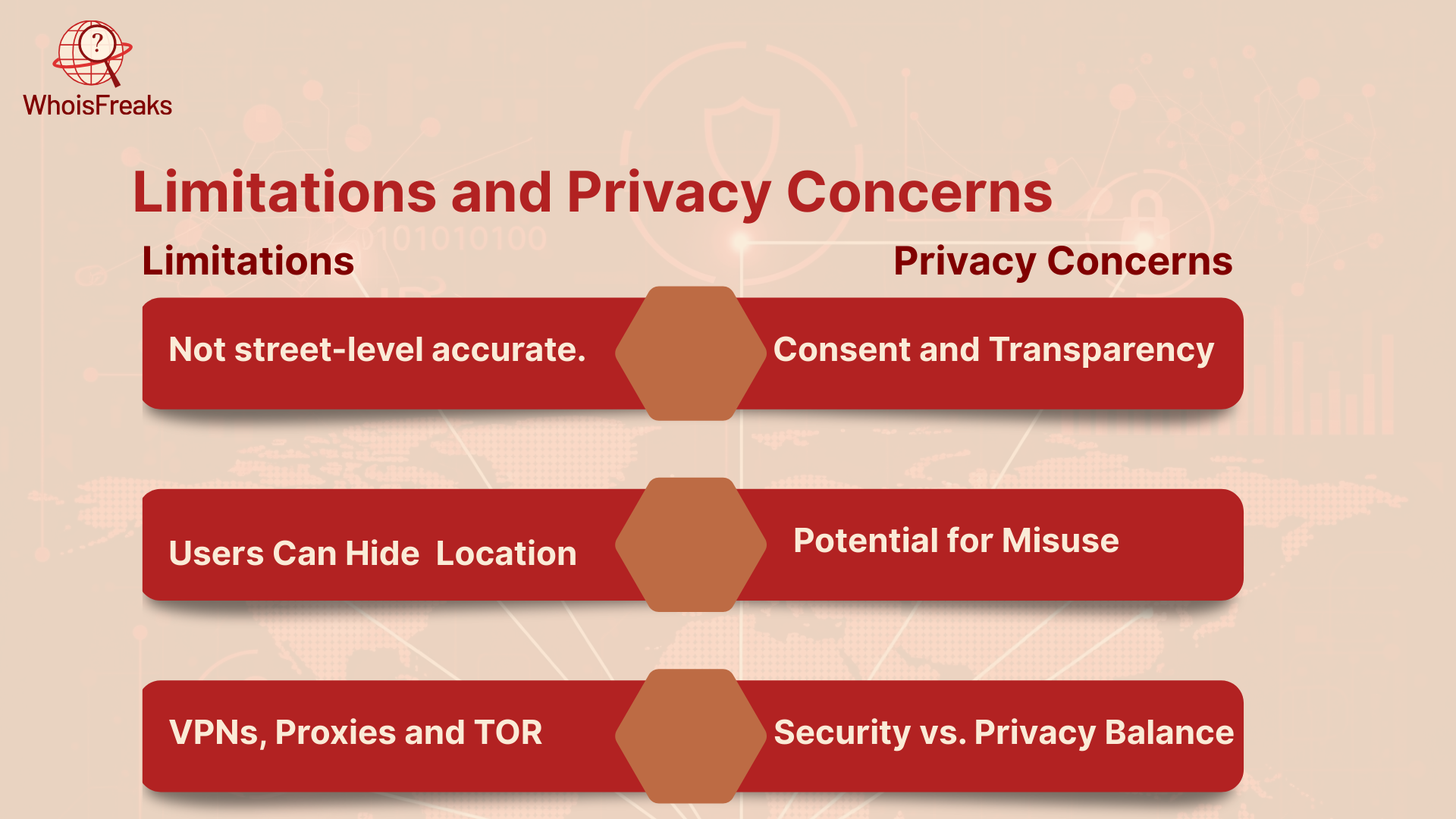
When using IP geolocation, it should not be lost in mind that though it is a potent instrument, it has its limits and gives rise to some privacy issues as well. This understanding will make the user to know and business to make use of the technology wisely.
IP geolocation cannot pinpoint an exact location. While it can accurately detect the country and provides reliable city-level data, street-level accuracy is not possible with any geolocation database service provider.
People can use tools like:
Such tools will conceal the actual IP address hence it is not easy knowing the actual location of a user. They are common in tracking down cybercriminals.
Although IP geo location does not tell ad-agencies your physical address, it is still able to access some generic details about you, including:
This raises some ethical and legal questions:
Where there are strict laws, such as EU (GDPR) or California (CCPA), websites have to make a notice to users that they are gathering information about the location.
If geolocation data is stored or shared improperly, it can be misused for collecting information without explicit user consent:
Although geolocation prevents fraud or attack on the users, can be used or practiced too much causing privacy violations. Companies have to find compromise between being safe and paying attention to user privacy.
IP geolocation may be a term that sounds technical, but in essence, it is a simple yet a powerful feature that makes the internet become more secure, intelligent and personal, more so on matters of IP geolocation understanding.
From showing content in your local language to blocking suspicious logins from the other side of the world, IP geolocation plays a quiet but vital role in how we interact online. For cybersecurity teams, it provides valuable location insights that help detect threats faster, stop fraud, and ensure compliance with legal standards.
But any technology has its challenges and this one has no exception. The problems with accuracy, the privacy protection, and the emergence of VPN imply that IP geolocation must be considered as one of the options of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, not the single protection measure.
Shaping a better understanding of the vulnerability of the digital sphere and improving the safety calculations, the system of IP geolocation can be understood by any student or by any technology analyst or cybersecurity expert.
Use your experience in practice by using the WhoisFreaks IP Geolocation API or use their Proxy testing tools Subdomain Lookup or Security Lookup. These tools are there to make you know how to come up with a secure app or even when doing an analysis of the suspicious traffic, smarter.

Historical WHOIS data is the digital fingerprint of domain activity. WhoisFreaks tools help security teams trace attackers, rebuild attack timelines, preserve court-ready evidence, and detect threats early, strengthening incident response and proactive cybersecurity defenses.
10 min read

Explore the benefits and risks of domain fronting, its applications, and how it impacts online privacy. Read the article for a comprehensive overview.
9 min read

Learn how to prevent subdomain takeover with essential strategies and best practices. Protect your online assets—read the full guide now!
8 min read