

By Qasim
Posted on May 20, 2025 | 13 min read
In today’s fast-paced digital world, cybersecurity threats, including cyber-attacks, are becoming more complex and widespread. Cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit weaknesses, which puts businesses, government agencies, and individuals at great risk. Because of this, it’s more important than ever to take proactive steps to protect against these threats.
One of the best ways to stay ahead of threat actors and cybercriminals is by using threat hunting. This involves actively searching for signs of suspicious activity in a network before an attack happens. Unlike traditional methods, such as firewalls and antivirus software, which respond to threats after they appear, threat hunting allows experts to find and stop potential threats before they cause harm.
A powerful tool in threat hunting is Reverse WHOIS. This technique allows cybersecurity experts to look at domain registration information to track down potential threats. By connecting domain names, registrant details IP addresses, and who owns them, experts can discover hidden links that may otherwise be missed.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at how Reverse WHOIS is changing the way cybersecurity professionals approach threat hunting. We’ll explore how the Reverse WHOIS API works, how WHOIS lookup helps with threat intelligence, and how law enforcement uses these methods to investigate cybercrimes. We’ll also discuss how Reverse WHOIS can be used to track down cybercriminals and reduce risks.
Reverse WHOIS is a special search tool used in the world of domain registration. It gives a fresh look compared to the regular WHOIS lookup. Normally, a WHOIS lookup helps users check details about a specific domain, like the owner’s name, contact details, and domain history. However, Reverse WHOIS turns this around. Instead of looking up information about a single domain name, it looks up all the domain names owned by a certain person, group, or email address.
Reverse WHOIS works by using a piece of info, such as an email or name, to find all the domain names linked to that information. This helps cybersecurity experts find hidden links between different domain names and other domains that might seem unconnected at first. This technique is very useful when trying to track bad actors across many websites, helping to give a better view of their actions.
While WHOIS lookup is good for finding out who owns a certain domain, Reverse WHOIS is much stronger when it comes to spotting patterns and tracking suspicious activity across many domains. It gives a deeper look into the online world, helping threat hunters and experts find large networks of potentially malicious domains.
Threat hunting is a proactive approach and method in cybersecurity. It involves experts searching for hidden threats within a network or system. Unlike regular security methods that rely on automated tools, threat hunting uses human skill to find threats that have not been spotted by machines. This human-led search, along with verifying contact details, is key for finding clever, hidden attacks that may slip past regular security systems.
Leveraging Reverse WHOIS in Threat Hunting can provide significant value to cybersecurity efforts.
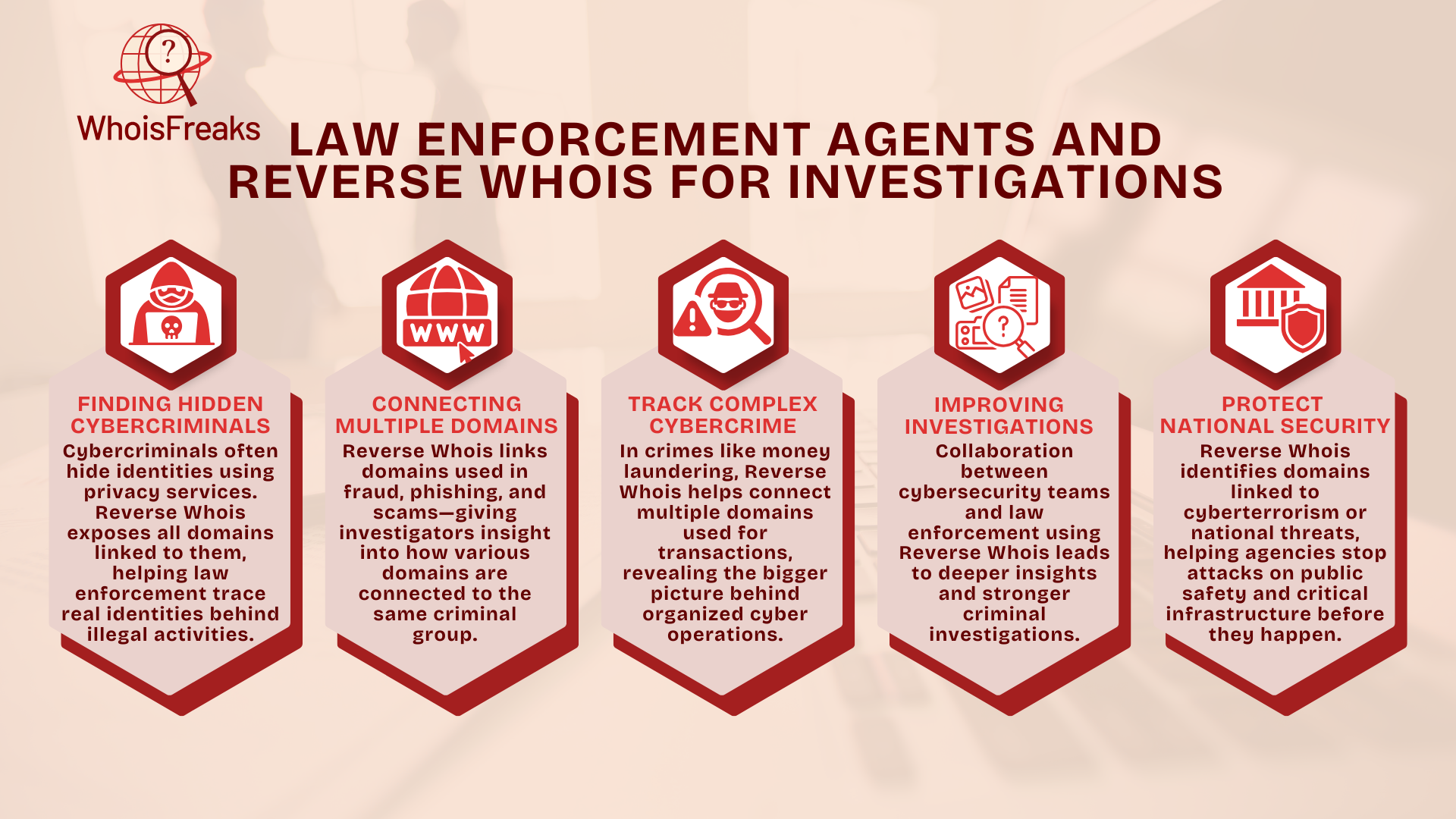
Cybersecurity experts use Reverse WHOIS as an important tool in threat hunting. It helps them find out more about bad actors and their actions. By uncovering all domain names tied to a suspicious email, name, or group, Reverse WHOIS allows experts and law enforcement agents to track down potential leads and the work of cybercriminals across many platforms. This information helps experts spot patterns that might be hidden at first.
Here’s how Reverse WHOIS aids in the process of threat hunting:

Cybercriminals often use many different domain names to carry out phishing, spread malware, and do other bad things. Reverse Whois helps experts find all the domains linked to a single person or group. This gives them useful information about the bad actor's methods and reach. For example, if an attacker registers many domains with the same email or organization name, experts can connect the dots and see their actions more clearly.
As part of their ongoing hunt for threats, cybersecurity experts regularly search for new domains that might be involved in harmful activities. By using a Reverse Whois search, they can compare new domains with past data to look for any suspicious connections. This helps experts find potential threats early, giving them the chance to act before an attack takes place.
Reverse WHOIS does more than just show the domains linked to one entity it also reveals hidden networks and links between different cybercriminal groups. By looking at who owns the domains found through Reverse Whois searches, experts can uncover shared services or group activities. This is important for finding larger networks of bad actors and understanding how they work together.
In the event of an ongoing or past cyberattack, Reverse WHOIS is useful for uncovering the full scale of the attacker's domain network. This allows cybersecurity teams to quickly check if the attacker has other domains involved in the same harmful operation. With this information, experts can respond faster and more accurately, helping to reduce any damage from the attack.
In the fast-changing world of cybersecurity, automation is key to improving the speed and accuracy of finding threats. One of the best tools for automating threat intelligence is the Reverse WHOIS API, which interacts with the WHOIS database. This service helps cybersecurity experts automatically search domain ownership data, uncovering hidden links between domains, people, and organizations that might otherwise be missed.
The Reverse WHOIS API lets experts quickly access a large amount of Reverse WHOIS data. Using an API (Application Programming Interface), cybersecurity professionals can gather and check domain info fast, without needing to search each domain one by one. This saves a lot of time and allows experts to focus on finding and fixing records of potential threats.
A Reverse WHOIS API is a service that allows users to interact with Reverse WHOIS databases automatically. By entering simple info like an email address, phone number, or company name, the API gives back a list of all the domains tied to that information. This tool helps security teams quickly find out about suspicious actors without needing to sort through a lot of domain registration data.
The Reverse WHOIS API is a game-changer for threat intelligence. It offers many benefits to cybersecurity experts:

Searching for links between domains and people by hand can be slow and may lead to mistakes. The Reverse WHOIS API makes this process automatic, letting security teams gather important domain ownership info in real-time. This helps save time and makes sure the data is correct, so experts can focus on analyzing and fixing problems, not just collecting data.
A big advantage of the Reverse WHOIS API is how it works with other cybersecurity tools. Many threat intelligence systems, like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), can easily use the data from Reverse WHOIS searches. This makes it easier for security teams to spot suspicious activity and act fast.
With the Reverse WHOIS API, cybersecurity experts can quickly spot new and growing threats. The API can automatically search for newly registered domains, helping teams stay ahead of cybercriminals who are always creating new domains for attacks. This proactive method helps companies block threats before they cause harm.
When working on big investigations, experts need to look at a lot of domain registration data. The Reverse Whois API can scale up to handle large amounts of data fast. Whether they are checking one bad actor or looking at a network of linked domains and their infrastructure, the API makes it easy to handle large investigations quickly and effectively.
WHOIS lookup is an important tool in cybersecurity. It gives key information about domain registration and ownership, including WHOIS records. While Reverse WHOIS helps find all domains tied to a specific person or organization, WHOIS lookup focuses on one domain at a time. This data is crucial for finding the owner of a domain and checking if it might be linked to harmful activities.
A WHOIS lookup is when you search a public database to get details about a specific domain name. This search gives important facts, such as:
WHOIS lookup is often the first step when experts investigate a suspicious domain. It helps them find important information to figure out if the domain is linked to harmful activities. Here's how WHOIS lookup helps with threat intelligence:
By doing a WHOIS lookup, experts can find out who owns a domain. They can then check if the details match those of a trusted company or person. If the domain belongs to someone suspicious or a known bad actor, it may get flagged for more investigation.
Cybercriminals often use many different domains for their attacks, like phishing and spreading malware. A WHOIS lookup helps find out where these domains come from and gives investigators key details. It helps find out if one person or group is using many domains for their attacks. WHOIS lookup also shows if the domain ownership has changed, which could mean the attack is still going on or is changing.
A WHOIS lookup can also show a domain’s past. It shows if the domain has changed owners before. If a domain keeps changing hands or has only been owned for a short time, it might be used for harmful activities. This could help experts find larger criminal networks or understand how the domain is being used.
The information from a WHOIS lookup can be checked against other sources, like IP addresses, URLs, and email addresses. This helps experts spot patterns of bad activity and get a clearer view of potential threats. By combining WHOIS data with other details, cybersecurity teams can better detect and stop attacks.
Threat hunting is a proactive approach in cybersecurity. Experts search for threats inside a network or system. Unlike other methods, it doesn't rely on alerts. It needs human skill to find threats missed by systems. One key tool in this hunt is Reverse WHOIS. It helps experts identify and find suspicious domains and track connections. By looking at domain registration data, Reverse WHOIS uncovers hidden patterns. These links may show malicious activity and help experts connect the dots.
Cybercriminals often use many domains for harmful acts. They run phishing campaigns, spread malware, and commit fraud. Reverse WHOIS helps trace these domains to the same owner. This gives experts a view of the attacker's actions. They may be using many platforms at once. This is helpful when looking at advanced persistent threats (APTs) or cybercriminal groups. With Reverse WHOIS, experts can see the attacker's infrastructure. It helps them understand the full scope of the threat.
Reverse Whois is also key in spotting new threats. It helps track newly registered domains linked to suspicious emails, phone numbers, or groups. By watching for these early signs, threat hunters can stop big attacks before they grow. Reverse WHOIS also tracks attackers who try to hide. They might use privacy protection or fake names for domains. But Reverse WHOIS still finds links between domains and shows clues about their tactics.
In an active attack, Reverse WHOIS is a critical tool. If a suspicious domain is found, experts use it to find others tied to the same owner. This helps them get a full view of the attacker's network. They can act quickly to stop the threat. When used with tools like Whois lookup, IP reputation services, and DNS monitoring, Reverse WHOIS makes threat hunting more effective against any attempt to breach security. It helps experts spot hidden patterns and find threats that might go unnoticed otherwise.
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is often used to organize Reverse WHOIS data because it can structure information in a way that’s easy for machines to read and understand. Each domain found in a Reverse WHOIS search is represented with specific records and tags that include registration details like the owner’s name, contact information, and key dates related to the domain's life cycle.
Cybersecurity experts rely on XML-formatted Reverse WHOIS data to automate their investigations, track domain histories, and spot patterns tied to suspicious activities. Its ability to handle large data volumes and integrate easily with other systems makes it an essential tool for proactive threat hunting and real-time analysis.
Reverse WHOIS is a useful tool that helps find hidden links between domains and threats in cybersecurity. But it does have its problems and limits. Knowing these issues, along with effective search terms, is important for cybersecurity experts who use this tool in their search for threats.

One big problem with Reverse WHOIS is that it might show incomplete or wrong data. Some domain owners use privacy services that hide their name and other details. This makes it hard to trace links between bad domains or people. Also, some WHOIS records may be old or not up to date, especially for domains that have been around for a long time. This can cause experts to miss important connections when looking for threats.
Another issue with Reverse WHOIS is data privacy and laws. Since it uses public domain registration details, it can cause privacy concerns. In places like Europe, there are strict laws, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), that limit what data can be shared. These rules can make it harder to get all the data experts need for a full investigation.
While Reverse WHOIS helps link domains to specific owners, it doesn't provide a full picture. It only gives data about the domain registration. It does not show other important details, like where the cybercriminal's IP address is or how they attack. To get the full story, experts need to use other tools along with Reverse WHOIS. This makes the job more complicated and takes more time.
Finally, another problem with Reverse WHOIS is false positives and overlapping data. Many businesses or people use the same domain registrar or hosting service. This can make it look like unrelated groups are linked. This can confuse experts and cause them to waste time checking false leads. They might miss real threats because of this overlap.
Reverse WHOIS is a strong tool for cybersecurity experts and law enforcement. It helps find links between domains, registrants, and organizations. This gives key insights for proactive threat hunting and investigation. When combined with other tools, Reverse WHOIS can uncover bad networks, track cybercriminals, and stop attacks before they do damage.
Even with its power, Reverse WHOIS has challenges. There can be incomplete data, privacy issues, and legal limits. It works best when paired with other cybersecurity tools. This gives experts a fuller view of threats. By combining Reverse WHOIS with other methods, experts can better fight cybercrime.
As cyber threats grow, Reverse Whois will stay important. It helps find new threats and keeps online systems safe. Its ability to spot hidden links between domains will keep supporting proactive security work. This makes it a key tool in the fight against cybercrime.

Historical WHOIS data is the digital fingerprint of domain activity. WhoisFreaks tools help security teams trace attackers, rebuild attack timelines, preserve court-ready evidence, and detect threats early, strengthening incident response and proactive cybersecurity defenses.
10 min read

Explore the benefits and risks of domain fronting, its applications, and how it impacts online privacy. Read the article for a comprehensive overview.
9 min read

Learn how to prevent subdomain takeover with essential strategies and best practices. Protect your online assets—read the full guide now!
8 min read