

Posted on April 10, 2025 | 21 min read
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a key part of the internet. It’s like the phonebook of the web. It turns easy-to-read domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand. This helps us do things online, like browsing websites or shopping. It makes the internet easy to use. But DNS has weaknesses that make it a target for hackers. Cyber threats like DNS spoofing, cache poisoning, and communication interception can happen. These attacks let hackers send users to fake websites or steal information.
To fix these problems, DNSSEC was created. DNSSEC is a strong security tool. It adds digital signatures to DNS records to make sure they are real and safe. It uses a private key to sign the data and a public key to check it. This stops fake data from showing up in DNS queries. It also prevents attacks like man-in-the-middle attacks, keeping the internet safe. DNSSEC is very important for things like banking, online shopping, and government websites to keep them safe. A hacked DNS in these areas can cause big problems.
But DNSSEC is not perfect. It has challenges in making sure all DNS queries are checked properly. However, it is a big step toward better internet security. It helps protect the internet from bad actors and makes it safer for everyone. In this article, we will dive deeper into how DNS and DNSSEC work and why they are crucial to our online safety.
A DNS server is a special computer that keeps a list of public IP addresses connected to website names. This helps it find the right IP address for websites like Fortinet.com or Yahoo.com. When people type a website name in their browser, the DNS server finds the correct IP address and takes them to the right website. The IP address then leads the device to the right website and makes sure the information can be shown.
Once the DNS server finds the right IP address, it lets the browser send data to content delivery network (CDN) edge servers or origin servers. These servers give the browser the website information. The process starts when the DNS server matches the website’s URL to its public IP address, allowing users to smoothly access the data they need.
The DNS system is designed to manage domain names. It is spread out and organized in layers to work well. This system makes sure it can grow, stay strong, and keep working even if some parts fail. At the start, Root DNS Servers are the first step. They help solve DNS queries. These servers send the queries to the right Top-Level Domain (TLD) servers. These TLD servers handle names like .com, .org, .net, and country code TLDs like .uk and .ca. Then, the TLD servers pass the queries to the authoritative DNS servers.
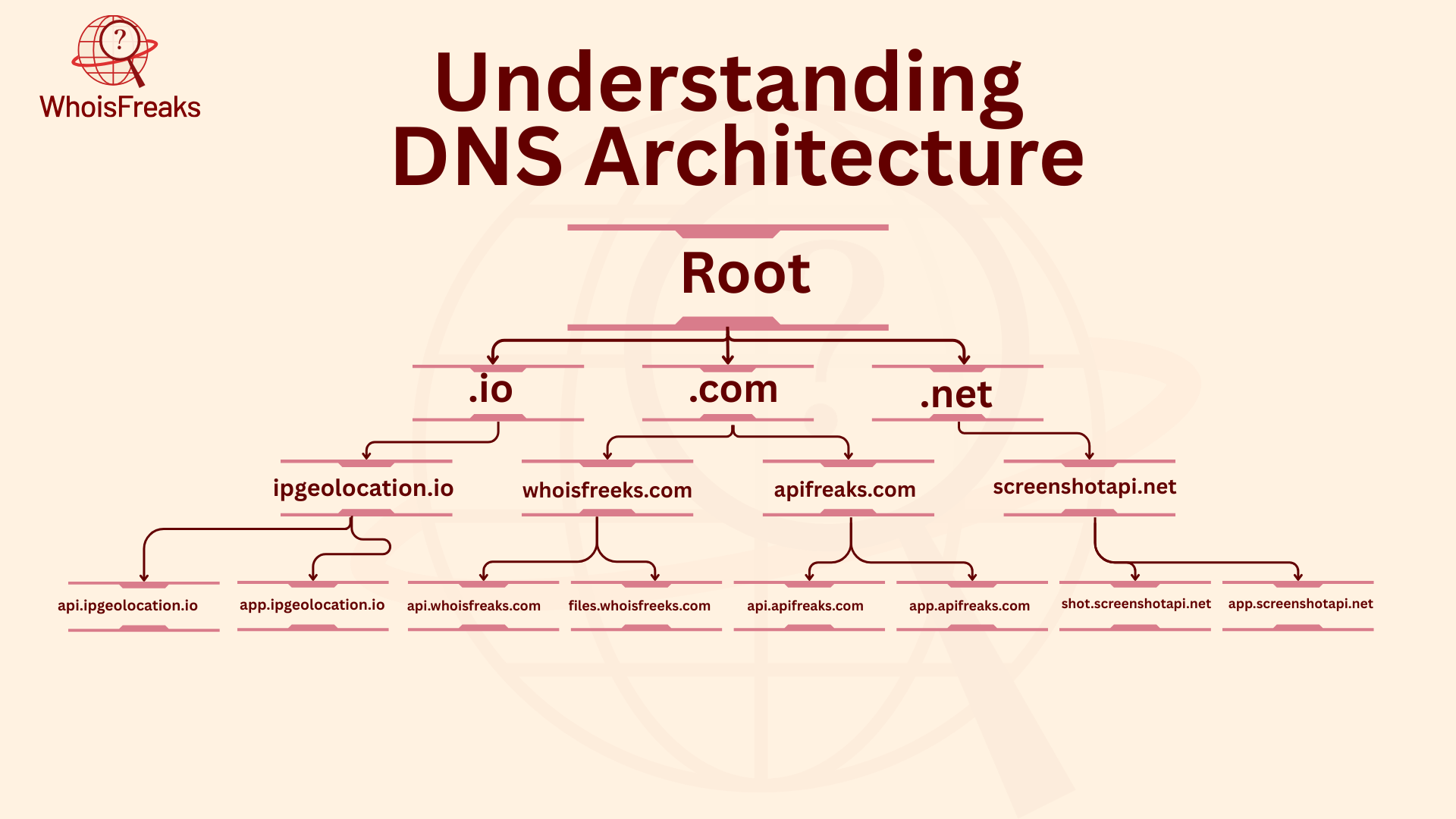
Every domain is part of a DNS zone, managed by a group or organization. In this zone, DNS records explain how the domain works. Some common records are:
Caching is important for speed. When a DNS query is solved, the result is saved by the resolver for a time called TTL (Time-to-Live). This saves time by not asking the same servers again. It speeds up the process for domains used often. But if the cache is not managed well, or data is old, it can cause security issues. Old data might be shown to users, which can be a risk.
The DNS system is set up with backups to stay reliable. Each domain has many authoritative DNS servers. If one server goes down, others take over. This way, DNS queries are always solved. This backup system helps keep internet services working, even if some servers are down.
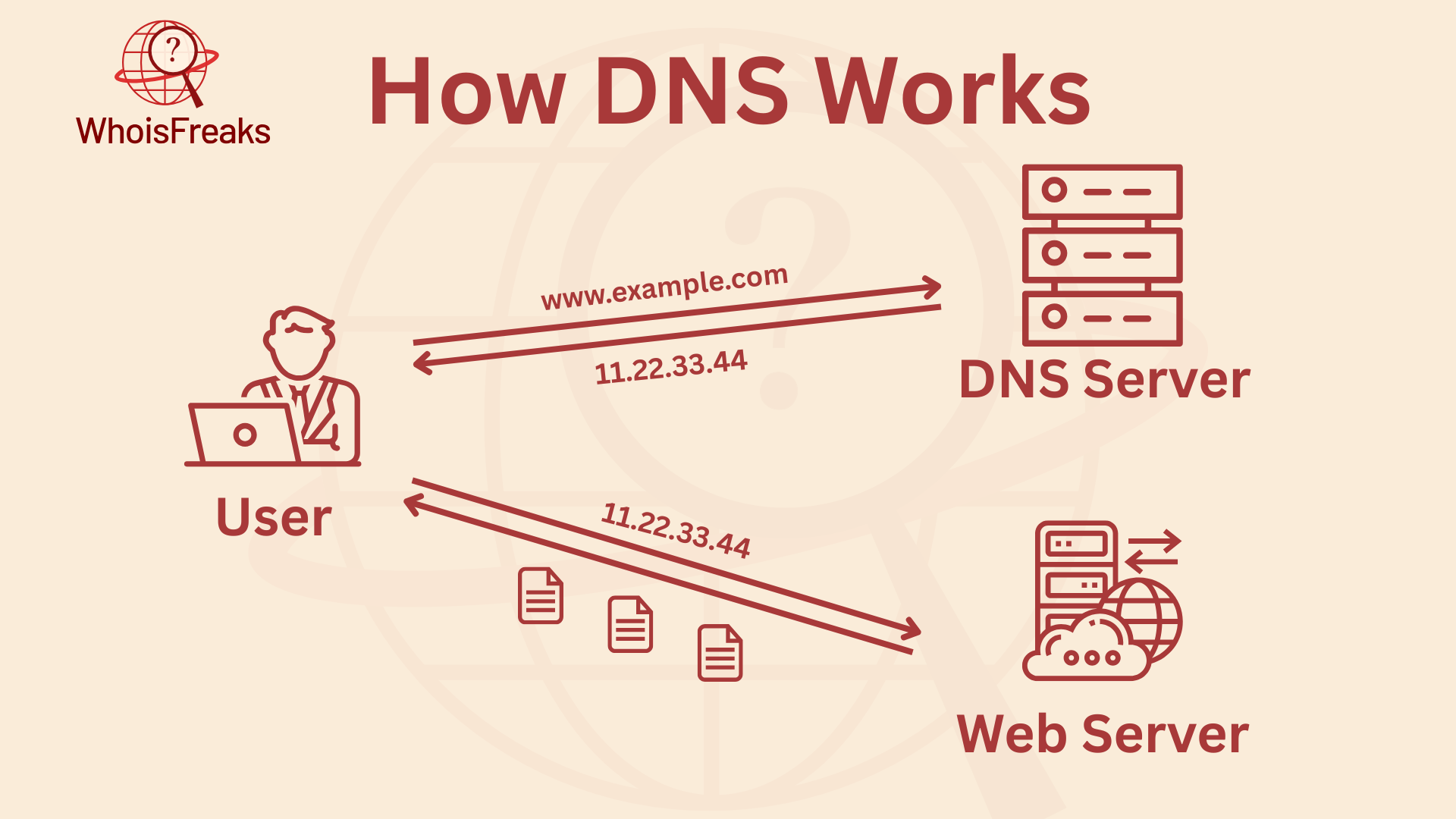
This whole process happens in just a fraction of a second, making it easy for users to reach websites without delay.
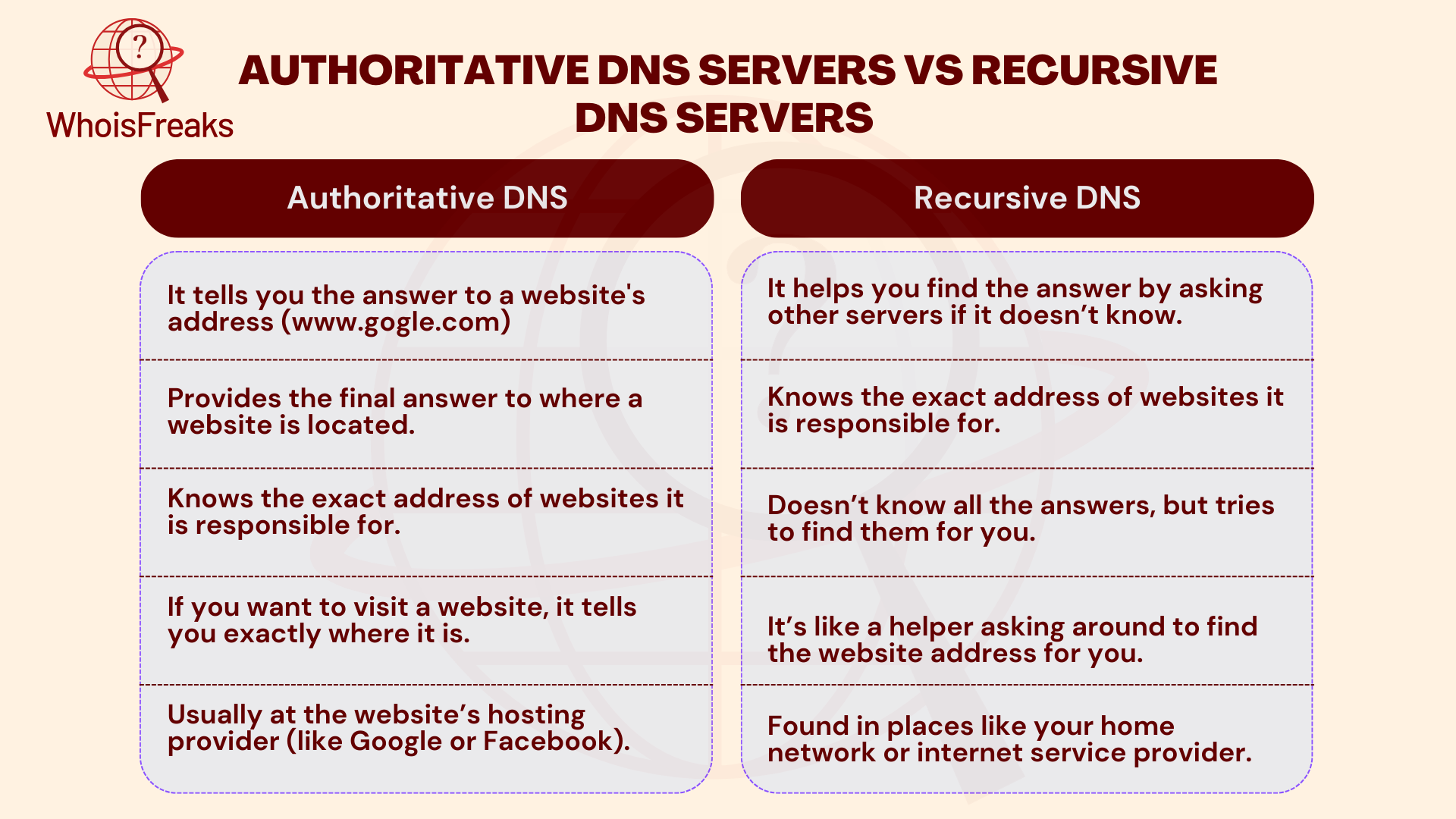
Here is the comparison of authoritative DNS servers and recursive DNS servers
DNS is crucial for the internet, but it can be a target for cyberattacks. Its open nature makes it vulnerable to many types of attacks. Securing DNS is important to protect users, businesses, and the whole internet.
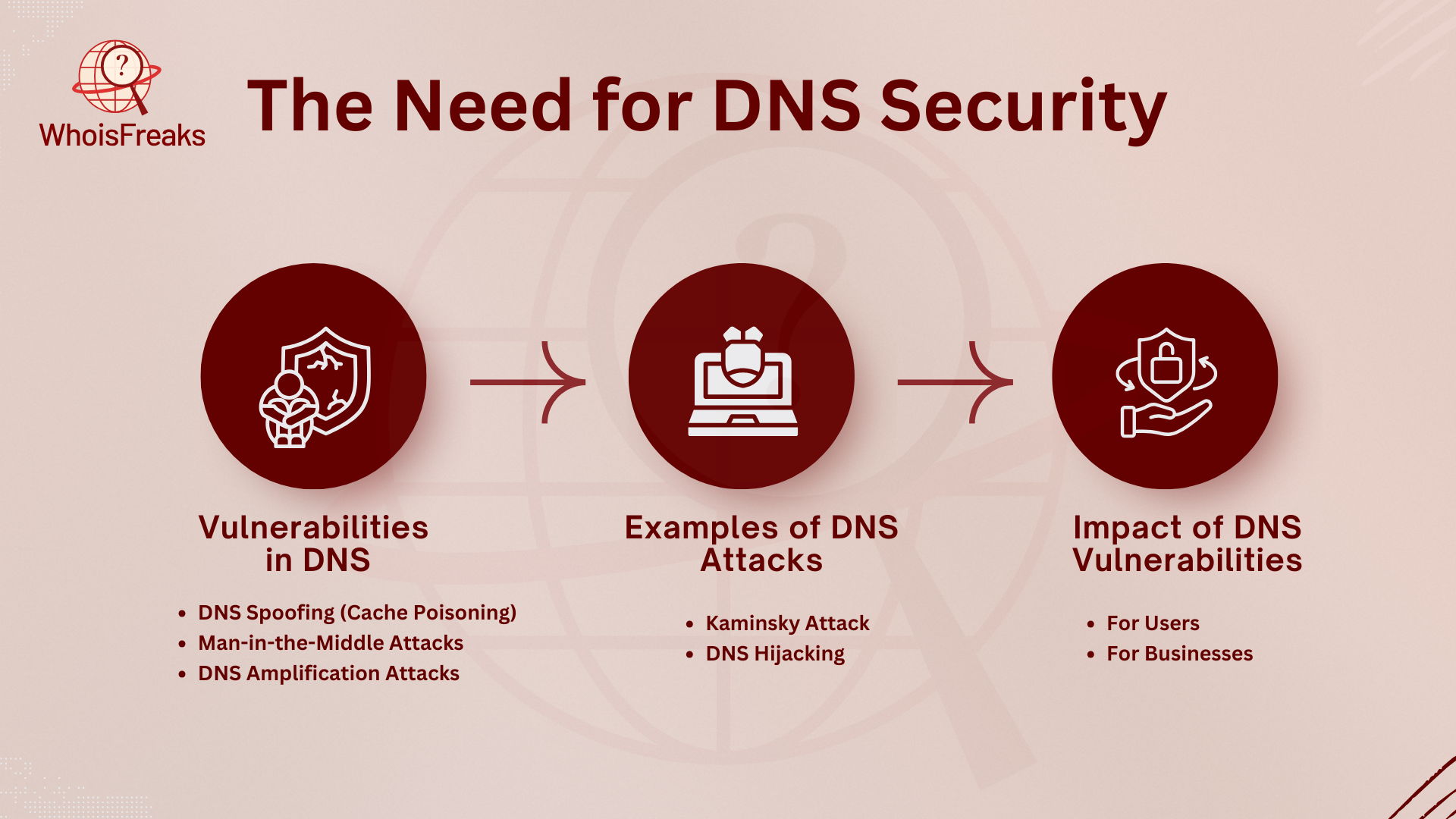
The basic DNS protocol lacks built-in security. This makes it open to attacks. Common types of attacks include:
One big example is the Kaminsky Attack in 2008. It used flaws in DNS caching. Hackers injected fake data into a DNS resolver’s cache, tricking users into visiting fake sites.
Another attack is DNS Hijacking. This happens when hackers take control of a domain’s DNS records, sending traffic to harmful sites. This can harm a business by damaging its online presence.
The effects of DNS attacks can be huge for users and businesses:
DNSSEC, or Domain Name System Security Extensions, is a security tool to fix the weaknesses in DNS. DNS has some problems that make it easy for attackers to cause issues, like DNS spoofing and cache poisoning. DNSSEC helps by adding cryptographic signatures to DNS records, which keeps the data safe and real.
When a DNS resolver asks a DNS server for data, it uses a private key to create a digital signature for the records. The resolver then checks the signature with a public key to make sure the data is not changed. If the signature is correct, the resolver knows the DNS data is real. If it's wrong, the resolver ignores the data, keeping users safe from harmful websites or DNS attacks.
DNSSEC adds extra protection to DNS by keeping data safe while it travels. It helps protect against cyber threats and makes sure DNS data stays accurate.
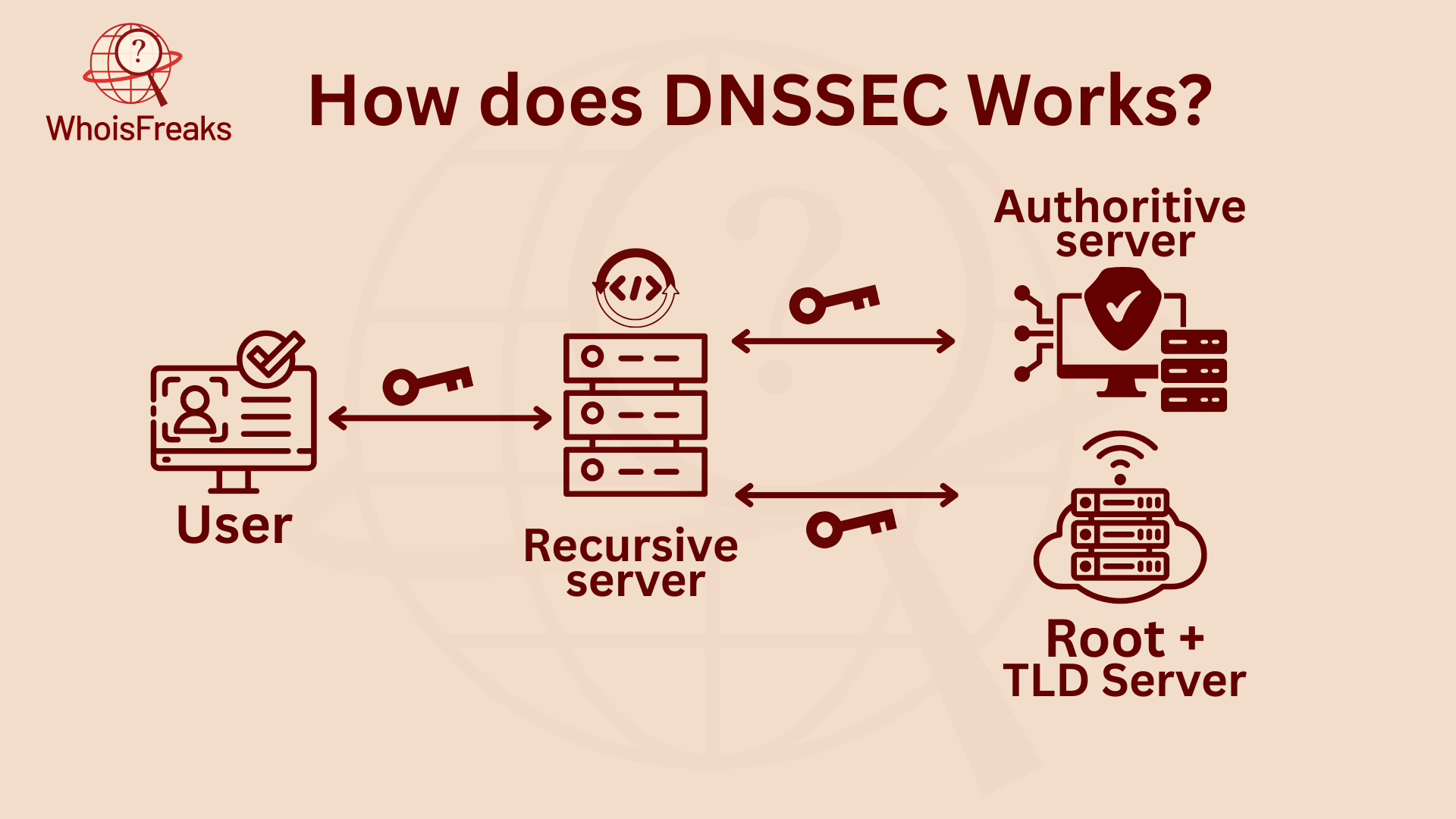
DNS security extensions (DNSSEC) make DNS more secure. It adds a strong layer to keep data safe. DNSSEC uses public key cryptography and private key pairs to make sure DNS data is real. A zone administrator creates digital signatures. These are stored as RRSIG records, using a private zone-signing key. This signature pairs with a public key and is shared as a DNSKEY record. This ensures that DNS data is secure.
When a DNS resolver asks for data, it gets the RRset and its RRSIG record. This record contains the private zone-signing key. The resolver then asks for the DNSKEY record to get the public ZSK key. To be sure the DNS response is real, the public ZSK's authenticity needs to be confirmed. This is done using key-signing keys (KSK).
The KSK signs the public ZSK and makes an RRSIG for the DNSKEY record. The name server shares the public KSK, just like the public ZSK. This forms an RRset with both DNSKEY records. These records are signed by the private KSK and checked with the public KSK. This ensures the public ZSK is real. This process makes sure the RRset is correct and safe. It helps keep the DNS data trustworthy.
DNSSEC is important for keeping the internet safe and stable. It works with groups like governments, businesses, and experts to make sure the Domain Name System (DNS) runs safely and smoothly.
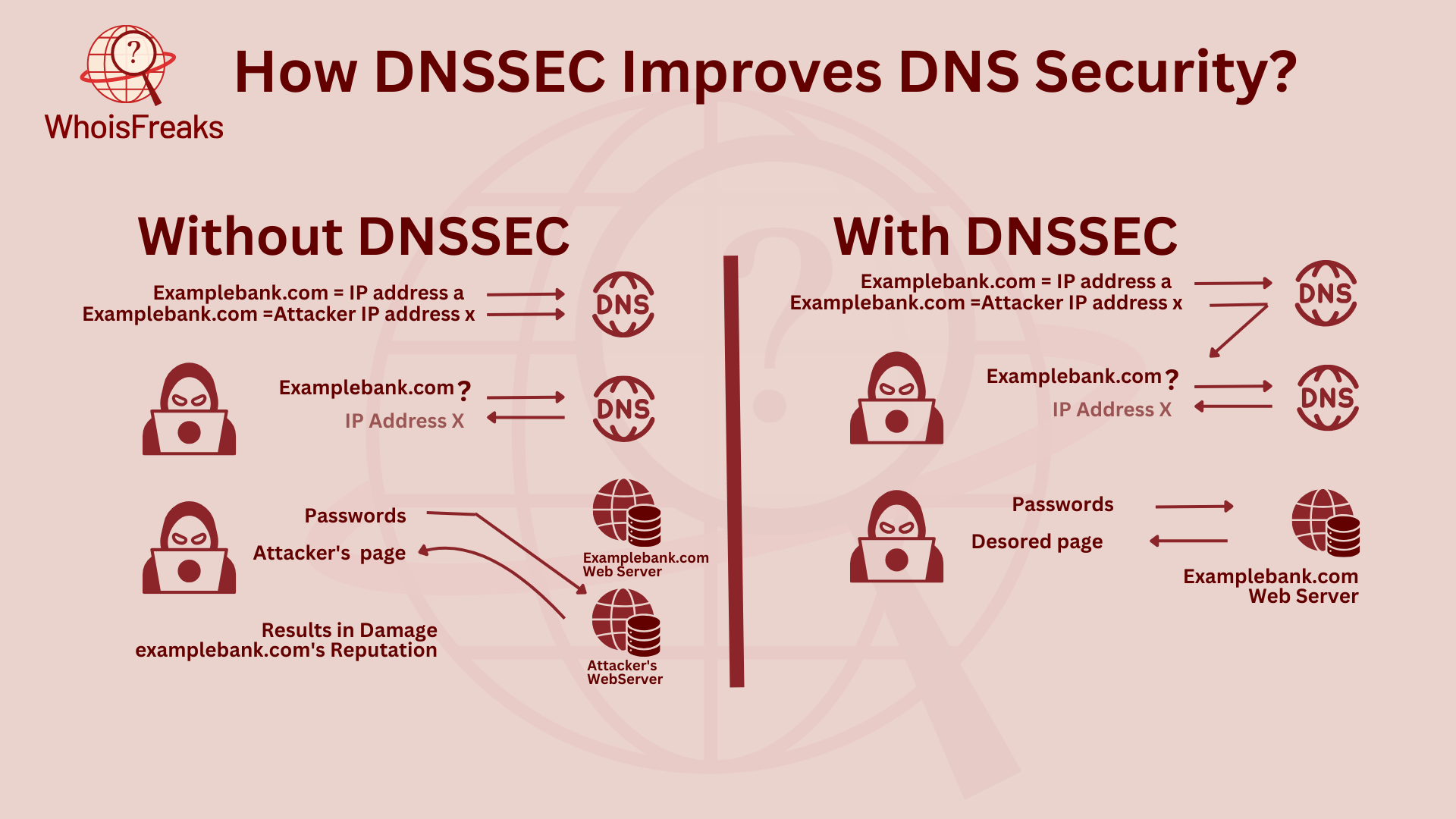
DNSSEC adds a strong layer of security to fix the problems in regular DNS. It adds cryptographic signatures to DNS records, making sure DNS answers are real. This stops attacks like DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, where attackers change DNS answers to send users to bad websites. With DNSSEC, digital signatures keep DNS records safe. This makes it hard for attackers to change or fake DNS answers. If a DNS answer is wrong, the resolver will spot the invalid signature and reject it. This keeps users from going to harmful sites.
DNSSEC also stops man-in-the-middle attacks. These attacks happen when hackers change messages between a user and a website. DNSSEC makes sure DNS answers are signed and checked, so the data stays safe. It stops hackers from changing messages while they move between the user’s resolver and the DNS servers. This extra safety keeps users on the right websites.
DNSSEC builds trust between DNS resolvers and servers. Every DNS answer is signed with a special key. The resolver checks this key to make sure the answer is real and safe. This trust helps reduce phishing and fake websites. By making sure users go to the right sites, DNSSEC helps keep the internet safe.
DNSSEC keeps DNS data safe by signing each record with a private key. This way, any changes to the data can be spotted by recursive resolver. If the data changes, the signature won’t match, and the resolver will reject it. This ensures that users get only correct and safe DNS information, which is key for safe internet use.
DNSSEC works by creating a strong chain of trust through the DNS system. This ensures the data is safe and real. It does this by signing DNS data at each level. The path starts at the root zone servers, moves to the top-level domain (TLD) servers, and then to authoritative DNS servers for each domain. Each link in the chain is protected with digital signatures. This forms a trust anchor that keeps the system secure.
To transfer trust from a parent zone to a child zone, Delegation signer (DS) records are used. When a resolver checks a child zone, the parent zone sends a DS record. This record holds a hash of the parent zone’s DNSKEY record. The resolver then compares it with the hashed public KSK from the child zone. If they match, the resolver knows the public KSK is real. This shows the records in the child zone are trustworthy. The system works smoothly from parent zone's private key down to zone, keeping the DNS chain of trust intact.
The table below shows a comparison between DNSSEC and DNS security
| Aspect | DNSSEC | DNS Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) adds security to DNS by making sure the responses are genuine. | DNS security refers to all measures that protect DNS from threats, including DNSSEC and other techniques. |
| Purpose | Protects against tampering with DNS data and ensures users are directed to the correct website. | A broad term that involves using different methods to protect DNS from threats like spoofing, cache poisoning, and attacks. |
| Focus | Focuses specifically on ensuring the integrity of DNS data by signing records. | Includes multiple methods, such as DNSSEC, firewalls, and encryption, to protect DNS systems. |
| Encryption | DNSSEC uses cryptographic signatures to validate the authenticity of DNS records. | DNS security may involve using encryption and other tools, but DNSSEC is the primary encryption method for DNS. |
| Implementation | Requires DNS providers and websites to implement DNSSEC for it to work. | DNS security involves a broader set of solutions and can be implemented in various ways (including DNSSEC). |
| Attack Protection | Protects against DNS spoofing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and cache poisoning. | It helps stop DNS attacks, including the ones DNSSEC blocks, and can also limit traffic or use firewalls for extra protection. |
| Widespread Use | Less common than basic DNS but gaining traction with websites and service providers. | It usually includes DNSSEC but can also use other security methods based on what’s needed. |
DNSSEC acts as a strong shield, keeping DNS answers safe. It helps stop DNS cache poisoning and spoofing. It uses cryptographic signatures to make sure DNS queries are real and not changed. This way, the DNS resolver only gets info from the trusted nameserver. This helps keep DNS data safe and stops fake websites from tricking users.
DNSSEC also lowers the chances of bad traffic redirection, which cybercriminals often use. Even though it can’t stop all threats like DDoS attacks, it still boosts online safety by making sure DNS answers are real. DNSSEC adds extra protection by checking that DNS data stays the same, making web browsing safer and more reliable.
DNSSEC is an enhanced security protocol designed to offer vital protection for sensitive DNS records. DNSSEC uses digital signatures that DNS servers check to ensure important records, like TXT and MX, are accurate and secure. This mechanism plays a pivotal role in safeguarding DNS data from potential threats.
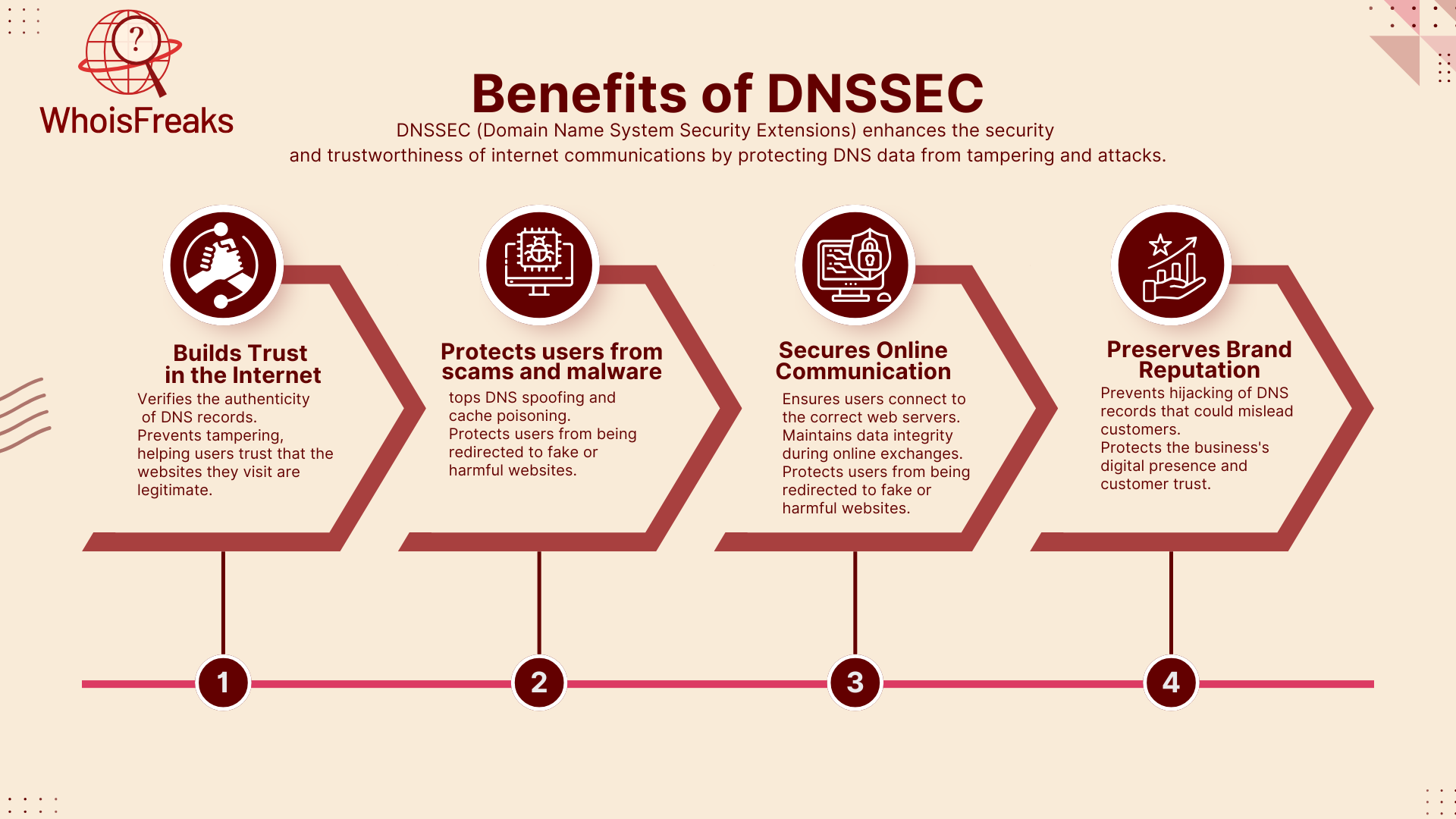
DNSSEC boosts DNS security by preventing fake DNS zones, especially those with important records. It's like having ships guard a treasure island, protecting valuable digital assets. With DNSSEC, our key online information is much safer, providing a more secure and trustworthy internet.
DNSSEC is very important for keeping the Domain Name System (DNS) secure and stable. It helps ensure the safety of the internet, and for it to work well, many groups need to work together. These groups include international organizations, governments, businesses, and tech experts.
DNSSEC is being used more and more in different industries because it helps keep DNS secure and protects users from cyber threats. It is very important for banks and government agencies, where trust and security are crucial for online services.
In the financial world, DNSSEC helps make sure users go to the right websites, lowering the risk of phishing attacks and fraud. For example, Bank of America and PayPal use DNSSEC to protect their websites. This stops attackers from making fake websites look real, keeping users and their money safe.
Governments worldwide know that DNSSEC is key to protecting their digital systems. In the U.S., for example, all .gov websites must use DNSSEC to improve cybersecurity. Similarly, The European Union urges countries to use DNSSEC on government websites to keep data safe from being changed or hacked. DNSSEC keeps important information safe, which is important for security and trust.
Many Top-Level Domains (TLDs) have started using DNSSEC to secure their websites. For example, Verisign, which manages the .com and .NET domains, began using DNSSEC in 2010. Big websites like Google, Facebook, and Twitter also use DNSSEC to protect their users from attacks. By using DNSSEC, these companies ensure their websites are secure, stopping attackers from redirecting users to harmful sites or stealing information.
There are several examples showing how DNSSEC works in real life to protect important systems. For example, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) started a program to make sure all federal websites use DNSSEC. In Germany, the government made DNSSEC mandatory for public websites to protect against cyberattacks. Japan also uses DNSSEC to secure government sites and banks, offering protection against DNS hijacking and other online threats.
As online threats continue to change, DNSSEC will play an even more important role in keeping the Domain Name System (DNS) secure. For the internet to remain safe and trustworthy, it’s important that more people adopt DNSSEC. Its development and use in future technologies will help protect the world’s digital infrastructure.

As the internet keeps growing, DNSSEC will be key to securing DNS data, especially with new internet technologies. The rise of IoT (Internet of Things), smart cities, and cloud computing relies on secure DNS to make sure communications are safe and trustworthy. As more devices and systems connect online, DNSSEC will become essential for keeping these connections safe and preventing hackers from attacking the DNS system.
With more IoT devices being used, there are new security risks because billions of connected devices could be vulnerable if DNS is not secure. DNSSEC will be important in making sure these devices can communicate securely and are protected from DNS attacks like fake websites or attacks that intercept data. Since IoT devices often share sensitive information, DNSSEC will help protect this data from bad actors.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and 5G networks also need secure DNS systems. Blockchain can benefit from DNSSEC by making sure blockchain systems trust the DNS data they use, while 5G networks will rely on DNSSEC to verify critical data and prevent attacks that could damage network security.
In the future, DNSSEC will be an important part of the overall cybersecurity strategies that companies use to protect their digital assets. While DNSSEC protects the DNS layer, it should work together with other security measures, such as TLS/SSL for encrypting data, firewalls to protect networks, and DDoS protection to stop large attacks. A complete security approach using DNSSEC and other technologies will create stronger defenses against complex cyberattacks.
As cyber threats continue to grow, DNSSEC will keep improving. Future updates could include better key management systems, faster performance optimization to reduce delays, and stronger connections with other security protocols. These changes will make DNSSEC easier to use and more effective at protecting the global DNS system.
To make DNSSEC and DNS security effective, organizations need to follow the right steps during setup, configuration, and maintenance. By doing so, businesses can protect their DNS system, reduce risks, and improve overall security.

When setting up DNSSEC, it’s important to:
Since DNSSEC depends on cryptographic keys, managing them properly is important:
DNSSEC setup needs teamwork:
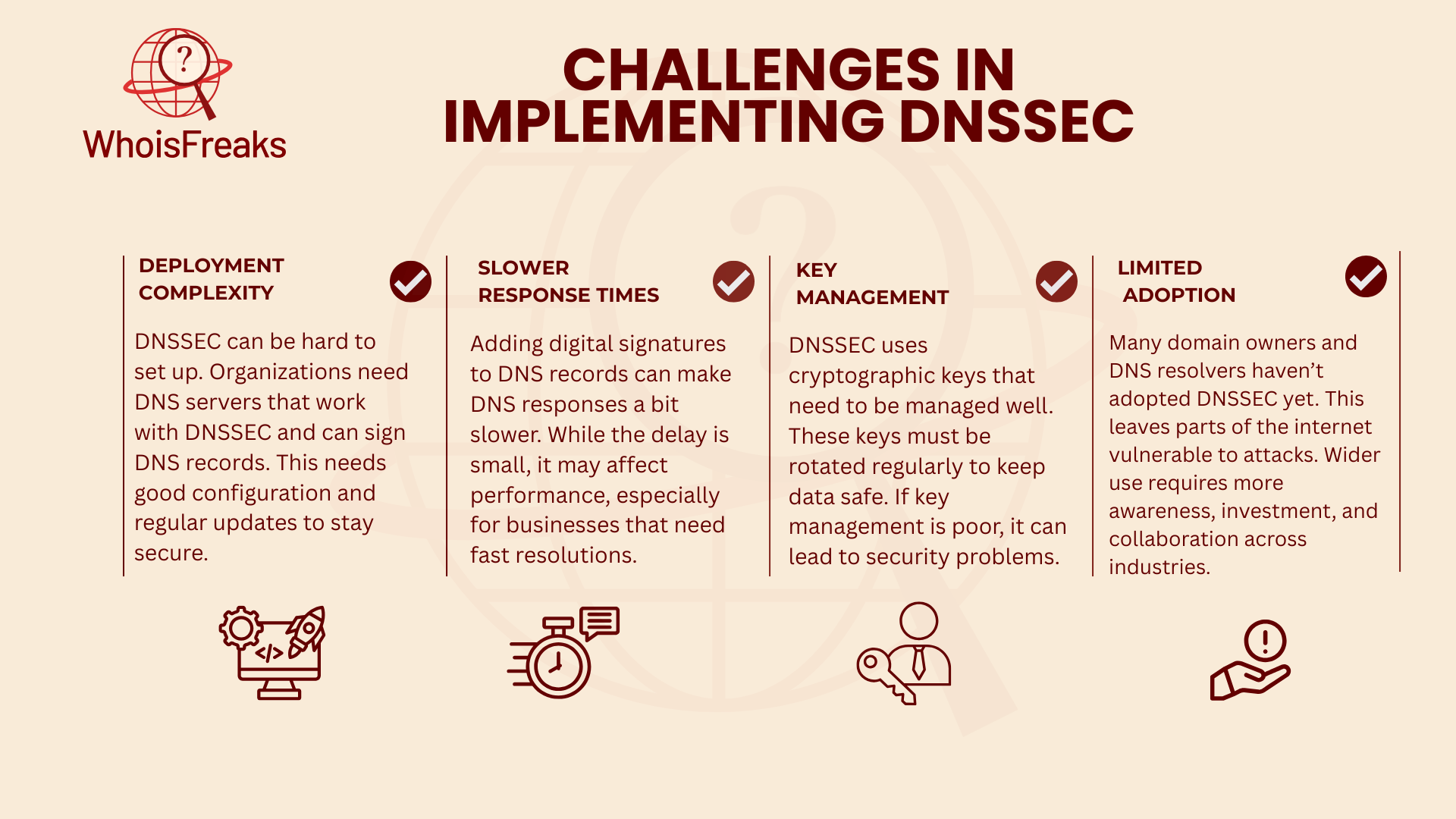
Even though DNSSEC has clear benefits, some misunderstandings about how it works can stop people from using it. It’s important to clear up these misconceptions so more organizations can adopt DNSSEC and understand its role in DNS security.
A common misunderstanding is that DNSSEC alone can fully protect DNS and stop all DNS-related attacks. While DNSSEC does improve DNS security by making sure the data is accurate and trusted, it doesn't protect against all types of attacks. For example, DNSSEC doesn’t encrypt DNS data (that’s done by protocols like TLS/SSL) and it doesn’t prevent attacks like DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service). To fully secure DNS, DNSSEC should be used alongside other security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
Another misconception is that DNSSEC makes DNS resolution much slower. While it’s true that DNSSEC adds an extra security check to the process, the speed difference is usually very small. With proper key management and optimization, the slowdown is barely noticeable. The added security benefits of DNSSEC far outweigh any tiny delays in DNS resolution.
Many think DNSSEC is too complicated to set up and manage. While setting it up does require configuring DNS servers, signing records, and handling keys, the process has become much easier thanks to DNSSEC-compatible DNS services and automated tools. With the right planning, implementing DNSSEC can be smooth. Many DNS hosting providers even offer DNSSEC as a default option, making it easier to use.
Some believe that only large organizations need DNSSEC. However, DNSSEC is useful for all kinds of organizations, even small businesses and individual domain owners. Smaller websites are still at risk of DNS attacks, and DNSSEC can help protect them. As more people adopt DNSSEC, it’s becoming a standard practice for all domain owners to use it.
While DNSSEC helps fix many weaknesses in traditional DNS, it’s not a complete solution for all DNS security problems. DNSSEC mainly stops attackers from changing DNS data and makes sure the responses are real. But it doesn’t solve problems like DNS amplification attacks or DDoS. To fully protect DNS, DNSSEC should be part of a broader security strategy, including DNS firewalls, traffic filtering, and DDoS protection.
In Conclusion, DNSSEC is key to keeping the Domain Name System safe. It makes sure DNS data is real and hasn’t been changed. As cyber threats grow, security measures like DNSSEC become more important. DNSSEC helps stop DNS-based attacks like spoofing, cache poisoning, and man-in-the-middle attacks. This helps keep the internet safe and builds trust in online services.
Though DNSSEC has its challenges, like needing careful key management, the benefits are worth it. It builds trust in DNS data and protects sensitive transactions. It also helps stop phishing and malware attacks.
As the internet grows and new tech like IoT, blockchain, and 5G rise, DNSSEC will be even more important. It helps secure DNS data, which is key for safe communication and transactions in digital systems.
Organizations and governments know DNSSEC’s importance and are using it for key domains. As more people adopt DNSSEC, the global internet infrastructure will be safer.
To get the best protection, DNSSEC should be part of a full security plan. It should work with other security tools like encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection. By using DNSSEC and following best practices, organizations can make their DNS security stronger and help keep the internet safe and trustworthy.

Discover essential insights on DNS poisoning and learn practical steps to safeguard your online presence. Read the article for vital protection tips.
10 min read

Learn how a DNS flooder can threaten your network security and discover practical measures to protect your systems. Read more to safeguard your network.
10 min read

Discover the essential role of DNS servers in internet functionality and learn how they enhance your online experience. Read the article for insights.
9 min read