
Understanding the Pharming Definition: A Guide to Cybersecurity Risks

By Qasim
Posted on May 06, 2025 | 13 min read


By Qasim
Posted on May 06, 2025 | 13 min read
Cybersecurity is always changing, and hackers are getting smarter with new ways to trick people online. One of these newer threats is called pharming a mix of the words “phishing” and “farming.” It’s a sneaky method used to steal personal information by sending users to fake websites that look like a legitimate website.
The big difference between pharming and phishing is that pharming doesn’t need the user to do anything, like click a link or open an email. Instead, hackers install harmful code on your device or network, which quietly redirects you to a fake site. Once there, any data you enter like passwords, bank info, or login details can be stolen.
In this article, we’ll explain how pharming works, go over the different types of attacks, and share tips on how to protect your business or personal data from a phishing attack. Keep reading to stay safe and understand why pharming is a serious threat in today’s digital world.
Pharming is a type of cyberattack were criminals trick internet users. They redirect users to fake sites, also called a fake or spoofed website. These fake sites are built to steal important information. The goal is to capture personally identifiable information (PII), like login details, passwords, social security numbers, and account numbers. Often, the aim of pharmers is identity theft, which can harm both individuals and businesses.
Pharming attacks usually target websites in the financial sector. These include banks, online payment platforms, and e-commerce sites. These sites handle sensitive transactions, making them a big target. The attackers may also try to install malicious software as part of the pharming malware on the victim’s computer. This malware gives them more access to data and can cause long-lasting harm. Pharmers take advantage of the trust users have in real websites, making pharming a growing threat to online safety.
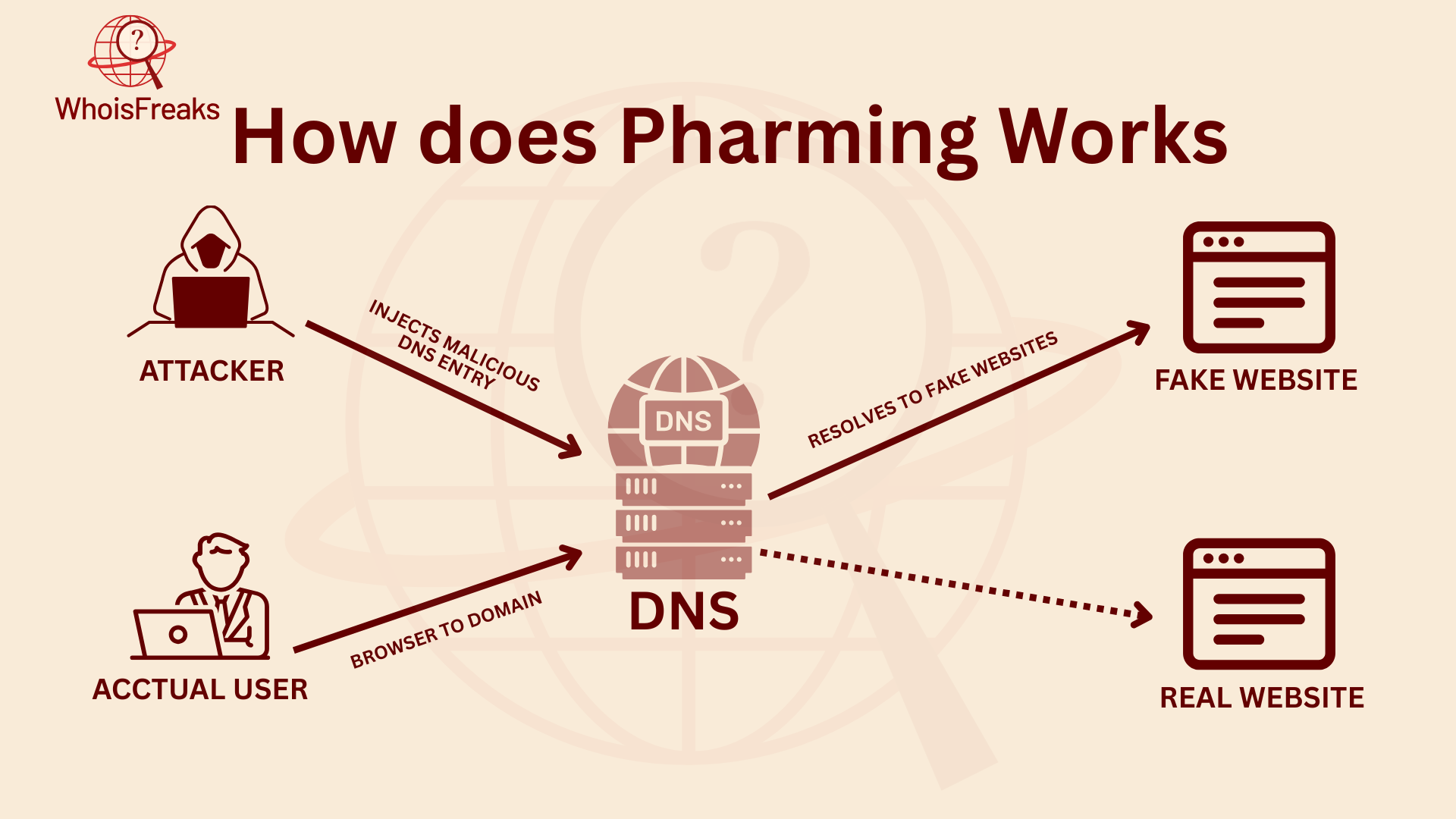
Pharming is a type of scam that tricks internet users into visiting fake websites. These fake sites are made to steal personal and financial details like login information, credit card numbers, and social security numbers. Attackers use different methods to carry out pharming attacks. They take advantage of weak points in the user’s computer, network, or DNS settings to make users go to these malicious sites. Here are some common methods used in pharming:
Malware infection is a big part of pharming. Bad programs like viruses, Trojans, and keyloggers can infect a user’s computer or network. These programs can change DNS settings or mess with the host file through DNS poisoning. This sends users to fake websites without them knowing. Once there, attackers steal sensitive info like passwords or credit card numbers. This can lead to identity theft or money fraud.
DNS cache poisoning is another way hackers attack. The Domain Name System (DNS) helps turn website names into IP addresses. Attackers can poison the DNS cache by messing with the mapping between website names and IP addresses. This makes users go to fake sites instead of the reputable DNS servers. These fake sites are designed to steal sensitive info like login details or credit card numbers.
Host file modification is another technique used by attackers. The host file is a local file on a computer that links website names to IP addresses. Attackers can change this file to alter DNS settings and send users to fake websites instead of real ones. Sometimes, this change happens in a local network, letting attackers' control where users go when they browse the web.
Rogue DNS servers are another trick used in pharming. Attackers can set up fake DNS servers or take control of real ones. When users try to visit a real website, they are sent to a fake one instead. These fake servers give wrong IP addresses, leading users to websites that steal personal and financial info. Attackers take advantage of users trusting real DNS servers to carry out these attacks and steal sensitive data by attackers exploit vulnerabilities.
Once users are redirected to fraudulent websites, they’re often prompted to submit sensitive information that the attackers then capture. The attackers exploit this information for various malicious purposes, such as identity theft, financial fraud, or unauthorized access to financial data.
Pharming attacks can be broadly categorized into two main types, each with its unique characteristics and methods of execution. Understanding each type helps to devise effective countermeasures:

DNS Server Pharming is a type of attack that targets DNS servers. Attackers use weaknesses in DNS software to send users to fake websites. These fake sites replace the real ones. Since DNS servers handle requests for many users, this can cause big problems for multiple users. If attackers take control, many users could be affected.
To stop these attacks, we can take a few steps. First, keep DNS software updated. This fixes known problems. Next, use DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) for extra protection. It stops changes that shouldn’t happen. Lastly, watch for unusual traffic. This helps find threats early and stop them.
Local Host Pharming is a type of attack. It uses weaknesses in DNS software. Attackers target DNS servers to send users to fake websites. These fake sites replace real ones. This can cause big problems for users. It messes up requests and sends people to fraudulent sites. When attackers control the DNS system, they can cause a lot of harm.
To protect against these attacks, a few steps can help. Using DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) adds extra security. It stops any unauthorized changes to DNS settings. Also, by monitoring your web browser and watching traffic patterns, threats can be spotted early. This helps stop attacks before they cause damage.
Both types of pharming attacks aim to deceive users and capture sensitive information, but they differ in their approach and impact. Awareness of these distinctions is crucial for both individual users and organizations.
Pharming attacks can have serious consequences for both individuals and organizations. These attacks can lead to financial losses and the theft of personal information, putting users and businesses at great risk.
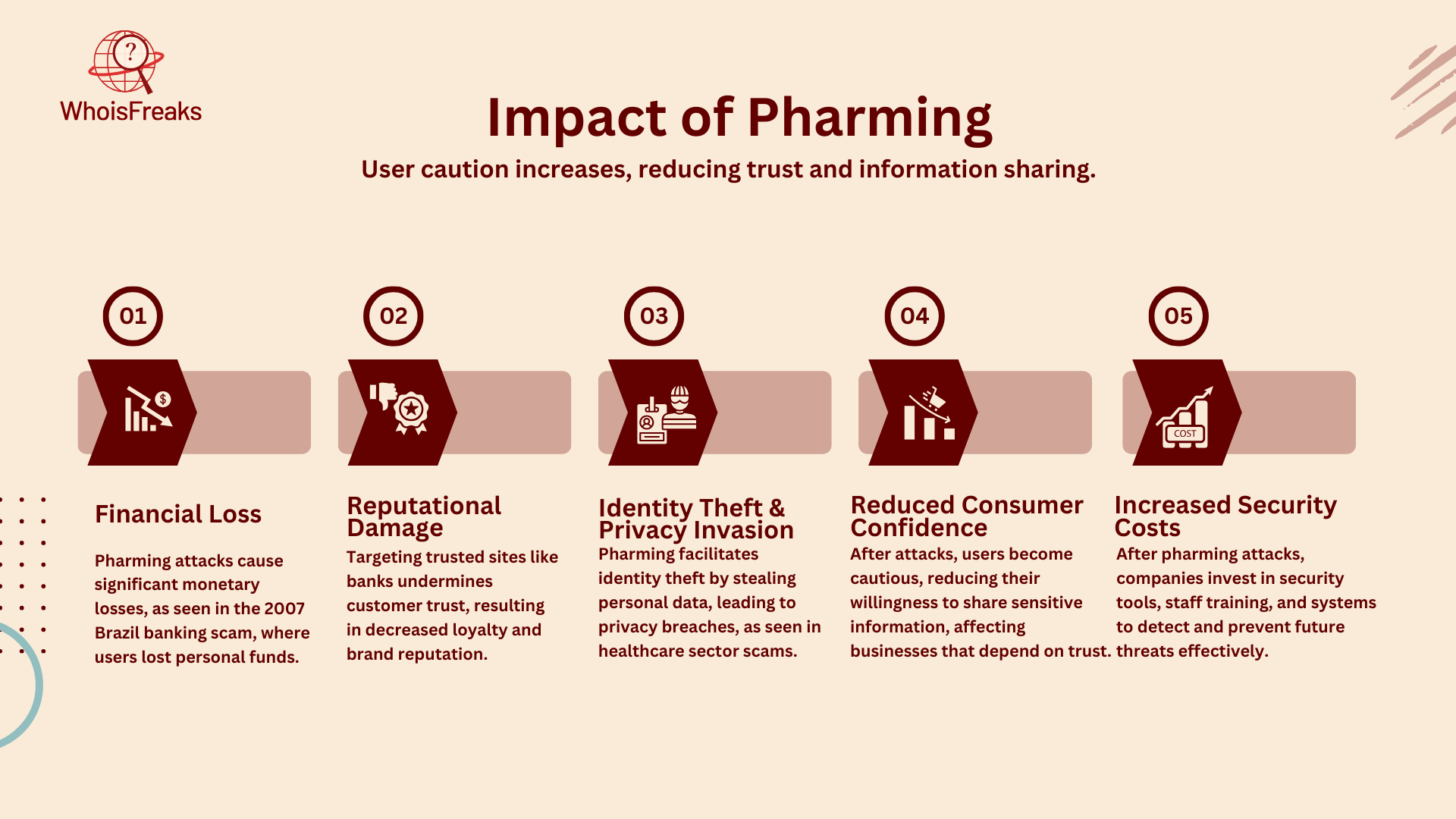
Pharming attacks can cause big money losses. In 2007, a pharming attack hit major banks in Brazil. Cyber criminals tricked users into visiting fake bank sites. Personal and banking info was at risk. Many people lost a lot of money. This shows how serious the financial impact can be.
Pharming attacks can damage a company’s reputation. Trusted sites like banks are often the target. When this happens, customers feel unsafe. This erodes trust and harms the brand. Customers start to question the safety of the site. Companies lose loyalty and business success as a result.
Pharming can lead to identity theft and privacy issues. In 2014, pharming scams targeted healthcare workers. Employees were tricked into using fake login pages. Attackers stole credentials and accessed private patient info. This caused serious identity theft problems. It shows the risks when personal data is stolen.
Pharming attacks have made people more careful online. Many now hesitate to share personal or financial info. This affects businesses that rely on online services. They have to rethink security measures to earn back trust.
To fight pharming attacks, companies need better security. They invest in cyber tools to find and stop these attacks. After DNS pharming hits, some banks spent more on anti-pharming tools. They also train employees to spot threats. This shows how much companies must spend to protect customers.
Recognizing the signs of a pharming attack can be difficult, but there are several red flags that you can look out for:
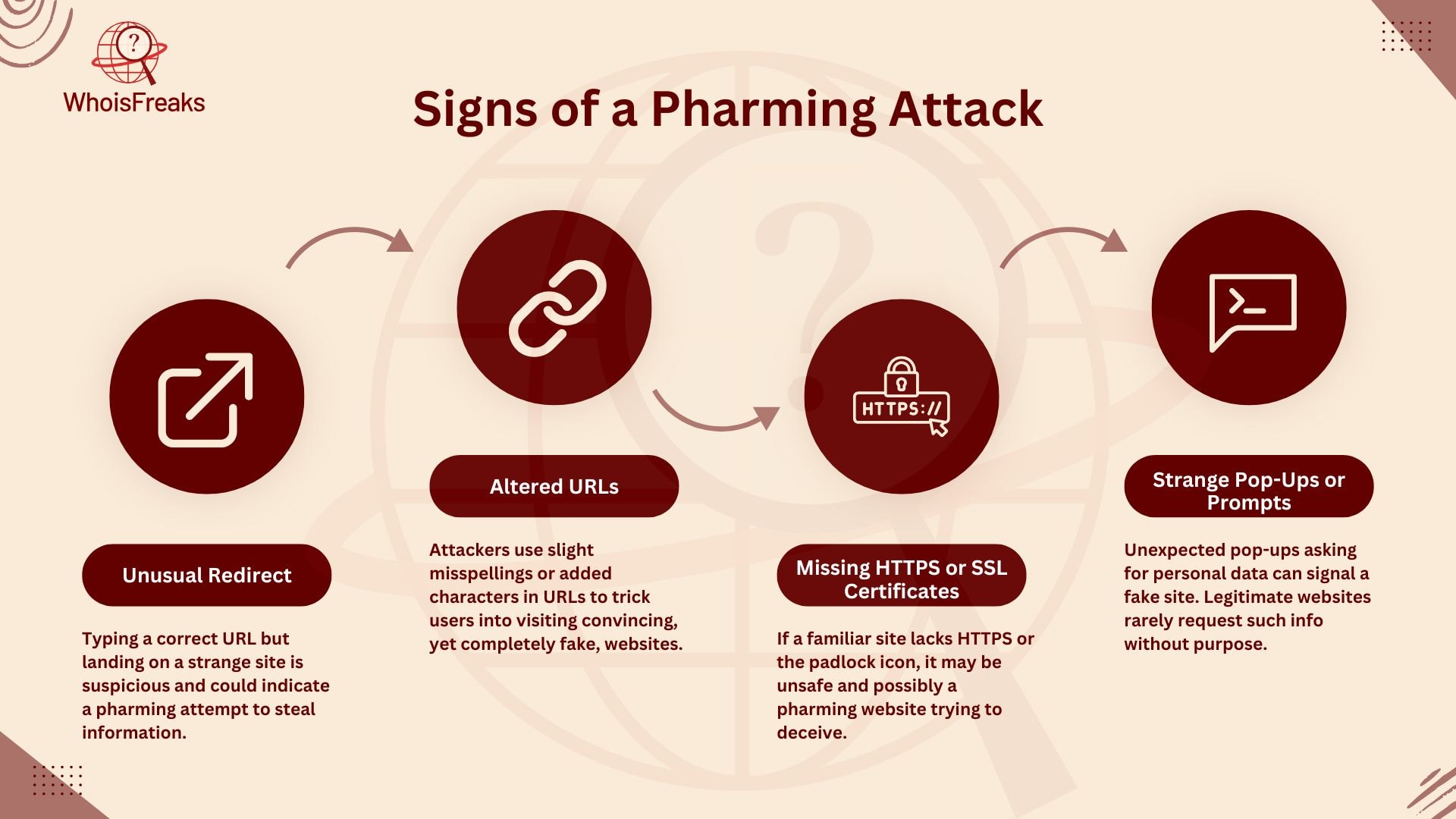
One sign of a pharming attack is an unusual redirect. If you type a familiar URL but are sent to a different site, it could be an attack. This should be a red flag, as it may lead to fake sites trying to steal your info.
Pharming websites often look like real ones. Attackers may change the URL by adding extra characters or misspelling words. These small changes can trick you into visiting a fake site that looks real.
Real websites, especially those with sensitive data like bank info, use HTTPS. If you see a familiar site without HTTPS or a padlock icon, it might be a fake site. Missing SSL certificates are a warning that the site is not safe.
Pharming sites might show strange pop-ups or prompts asking for personal details. These are not normal for real sites. Be careful when a site asks for your info, especially if it seems unnecessary. This could be a trick to steal your data.
By watching out for these signs, you can avoid falling for a pharming attack.
| Aspect | Phishing | Pharming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fraudulent emails trick users into visiting fake websites to steal personal info. | A type of phishing where hackers install malicious code on your device to redirect you to fake websites. |
| How it works | Cybercriminals send emails with fake links asking for personal details. | Hackers install malicious code to automatically redirect you to fake sites without needing a click. |
| Requires user action | Yes, the user clicks a link in an email, text, or social media message. | No, it happens automatically without user interaction. |
| Targeted methods | Emails, social media, or text messages that ask for sensitive info. | Malicious code installed on the device or server redirects you to fake websites. |
| Danger level | Less dangerous because it relies on user action. | More dangerous as it can affect many users without them knowing. |
| Prevalence | More common and easier for attackers to carry out. | Less common due to the complexity of setting up the attack. |
Pharming can be very risky for both people and businesses. Attackers can steal sensitive data like login info, credit card numbers, and social security numbers. This can lead to identity theft, where attackers use stolen personal details to commit fraud. The stolen data can also be used for financial fraud, such as draining bank accounts or making unauthorized purchases. Pharming attacks often target banking websites and online payment sites, where they can redirect users to fake sites, raising concerns in a phishing vs context to steal this sensitive information. Attackers can secretly siphon money from victim accounts without detection.
For businesses, pharming can cause big data breaches. This puts customer data, company secrets, and other important information at risk. Once hackers get this data, they may use it for their own gain or sell it. These breaches can severely hurt a company’s reputation, causing customers to lose trust in the business. When this happens, the business may face legal action and big financial losses. Recovering from such an attack can be expensive and time-consuming, as businesses work to fix the damage caused by the attack.
Avoiding a pharming attack is similar to protecting your devices from viruses or malware. Here are some practical steps and best practices to keep you safe:
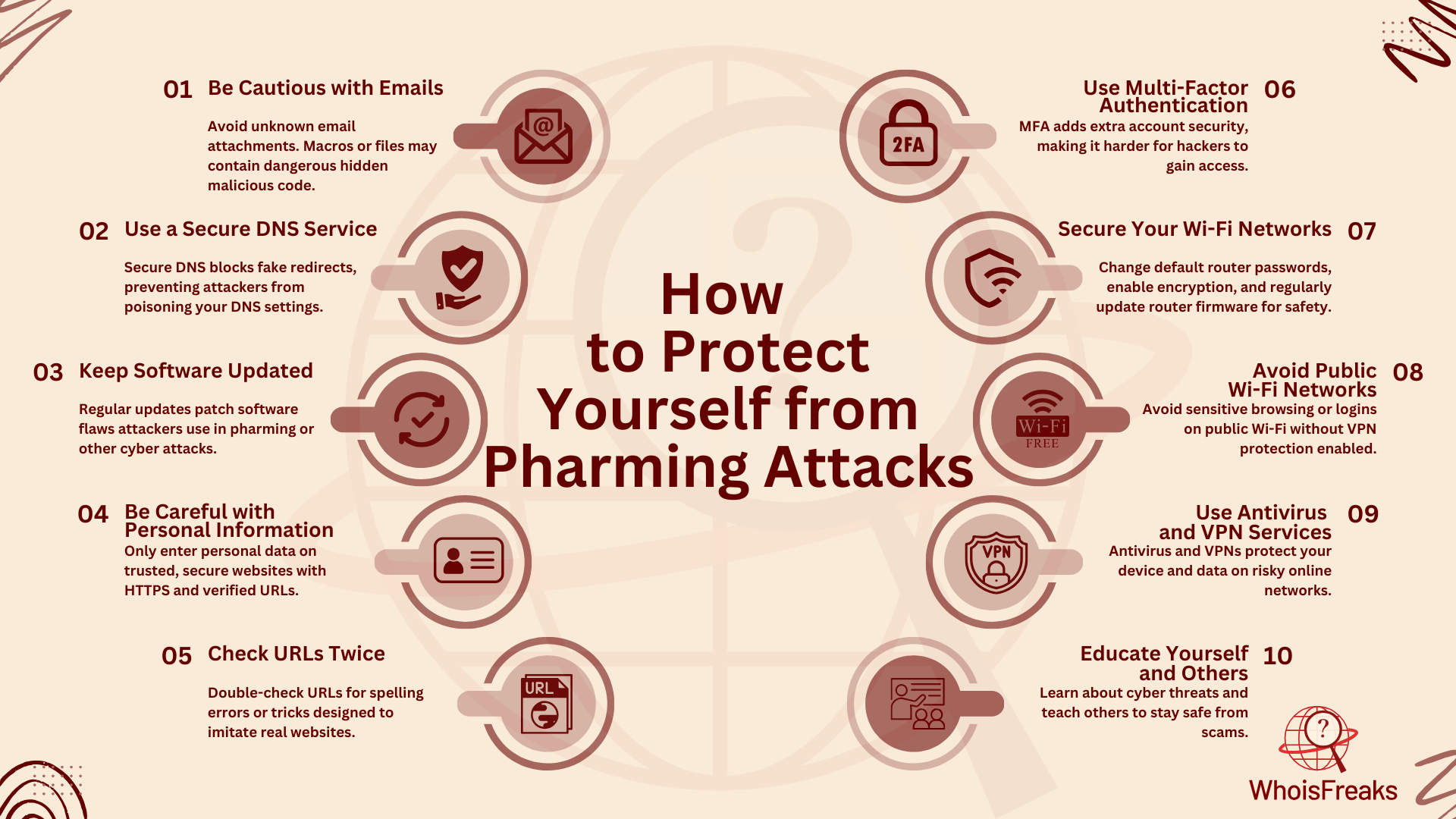
By following these steps and staying aware of potential risks, you can greatly reduce your chances of falling victim to pharming attacks and protect your personal information.
Pharming attacks have caused major security issues for both individuals and businesses. Here are a few high-profile pharming attacks that show just how dangerous this kind of cybercrime can be:
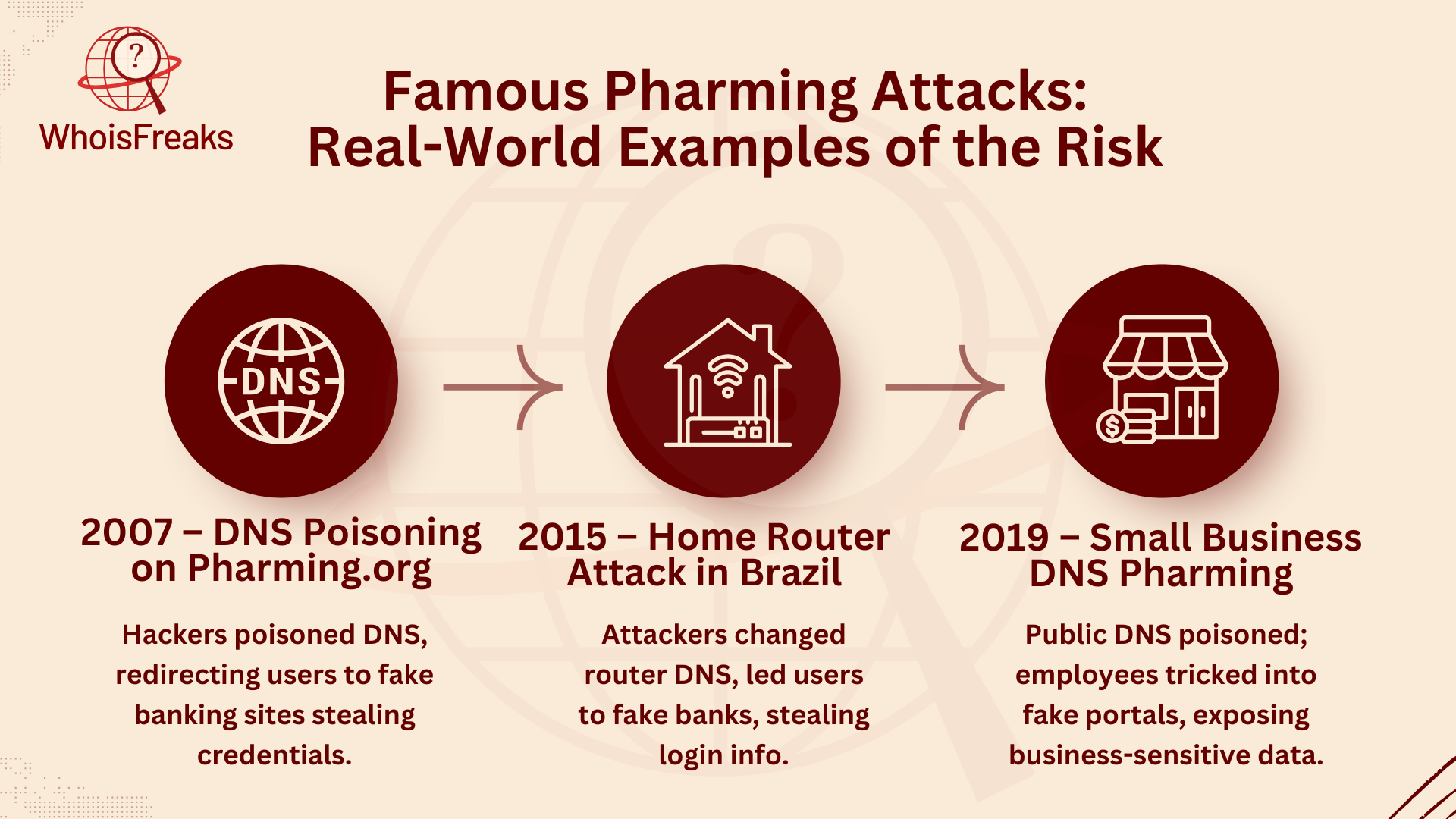
In 2007, cybercriminals attacked a large group of internet users by poisoning a major DNS server. This caused thousands of users to be automatically redirected to fake banking websites, where their login details were stolen. The attack revealed weaknesses in DNS security, which led to more focus on protecting DNS vulnerabilities.
In 2015, attackers in Brazil targeted home routers by changing the DNS settings. This redirection led users to fake versions of popular banking websites. As a result, many victims unknowingly gave away their banking login credentials to hackers. This attack showed how important it is to secure router DNS settings.
In 2019, attackers targeted small businesses by poisoning public DNS servers. When employees tried to log in to their company websites or email portals, they were sent to fraudulent versions of those sites. This allowed the attackers to steal login credentials and other sensitive business information. This incident highlighted the damage that DNS-based pharming can cause to companies, no matter their size
Pharming attacks present serious risks to both individuals and businesses, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, data breaches, and reputational damage. These attacks can target sensitive information, such as login credentials and credit card numbers, and redirect users to fake websites without their knowledge. As technology evolves, so do the tactics of cybercriminals. It’s important for both individuals and businesses to stay vigilant and adopt strong security measures, such as using HTTPS, monitoring for unusual traffic, and investing in anti-pharming tools. By staying aware of the signs of pharming and taking proactive steps, we can better protect ourselves and our information from these harmful attacks.

Historical WHOIS data is the digital fingerprint of domain activity. WhoisFreaks tools help security teams trace attackers, rebuild attack timelines, preserve court-ready evidence, and detect threats early, strengthening incident response and proactive cybersecurity defenses.
10 min read

Explore the benefits and risks of domain fronting, its applications, and how it impacts online privacy. Read the article for a comprehensive overview.
9 min read

Learn how to prevent subdomain takeover with essential strategies and best practices. Protect your online assets—read the full guide now!
8 min read